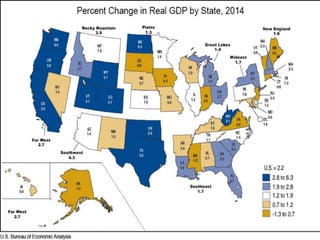
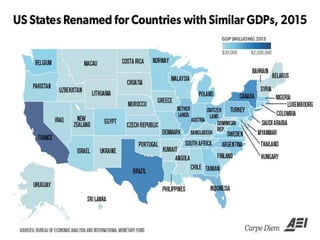
This document discusses key concepts related to government spending and taxation in the United States. It defines Gross Domestic Product (GDP) as the total value of goods and services produced, and notes that 34% of all government spending is funded through GDP. It also defines Gross State Product (GSP) and Gross Regional Product (GRP) as measures of economic output for states and regions. The document outlines various taxes levied by federal, state, and local governments, including income, sales, property, corporate and excise taxes. It also discusses principles of taxation such as equity, yield, elasticity, political accountability, and acceptability.