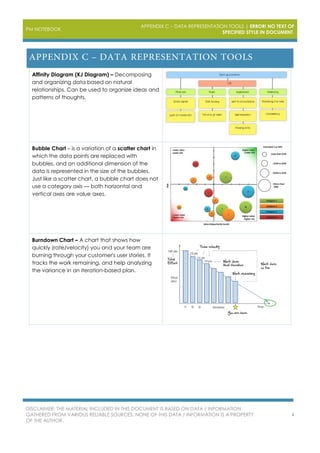
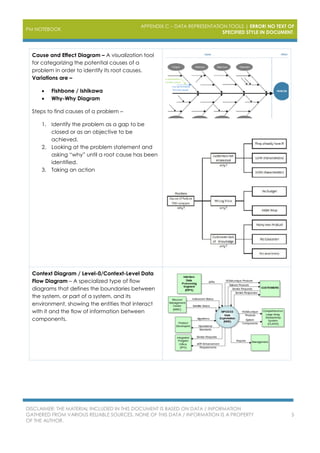
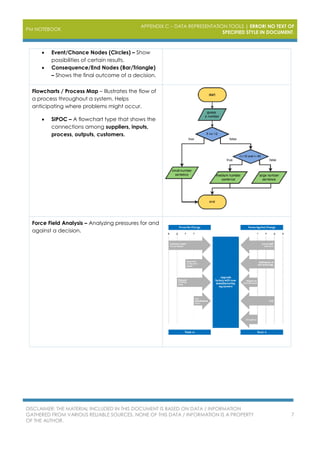
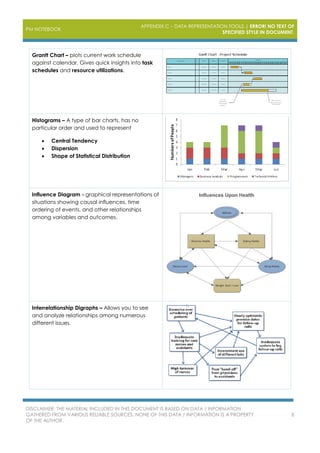
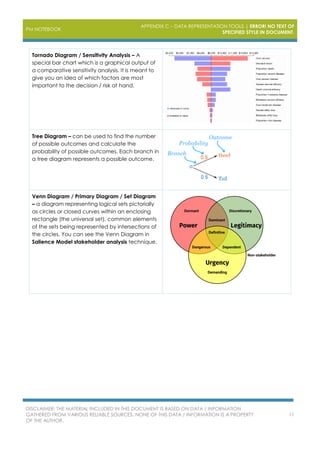
The document outlines various project management data representation tools essential for the PMP exam, including affinity diagrams, burndown charts, control charts, and Gantt charts. Each tool serves to analyze and visualize different aspects of project management, from idea organization to decision-making processes. It emphasizes the importance of utilizing these tools for effective project management and risk analysis.