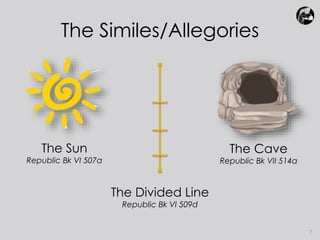
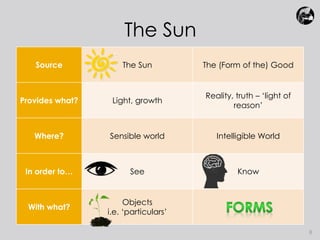
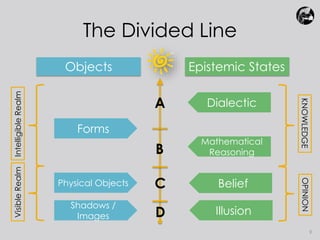
Plato believed that true knowledge comes from comprehending eternal, unchanging forms/ideas that represent concepts like beauty, justice, and goodness. He used three similes - the Sun, the Line, and the Cave - to explain his Theory of Forms. The Sun simile portrayed the form of the Good as the source of truth, like the sun provides light. The Line simile depicted different levels of understanding moving from images to forms. The Cave simile represented people trapped in a cave seeing only shadows on the wall, unable to comprehend true reality outside. Plato used these similes to illustrate his view that true knowledge comes from rational understanding of the forms, not from sensory experience.