Embed presentation
Downloaded 20 times


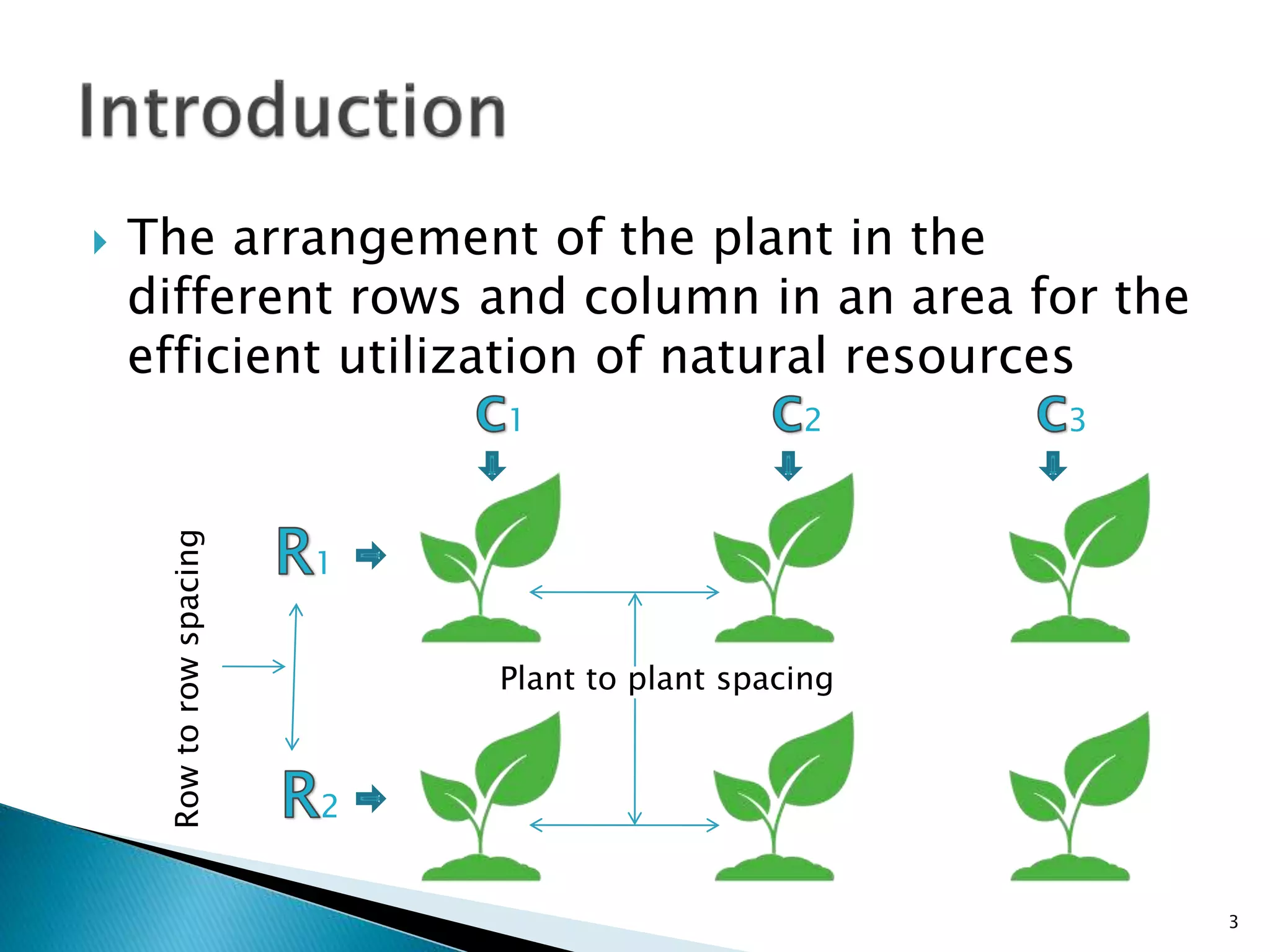

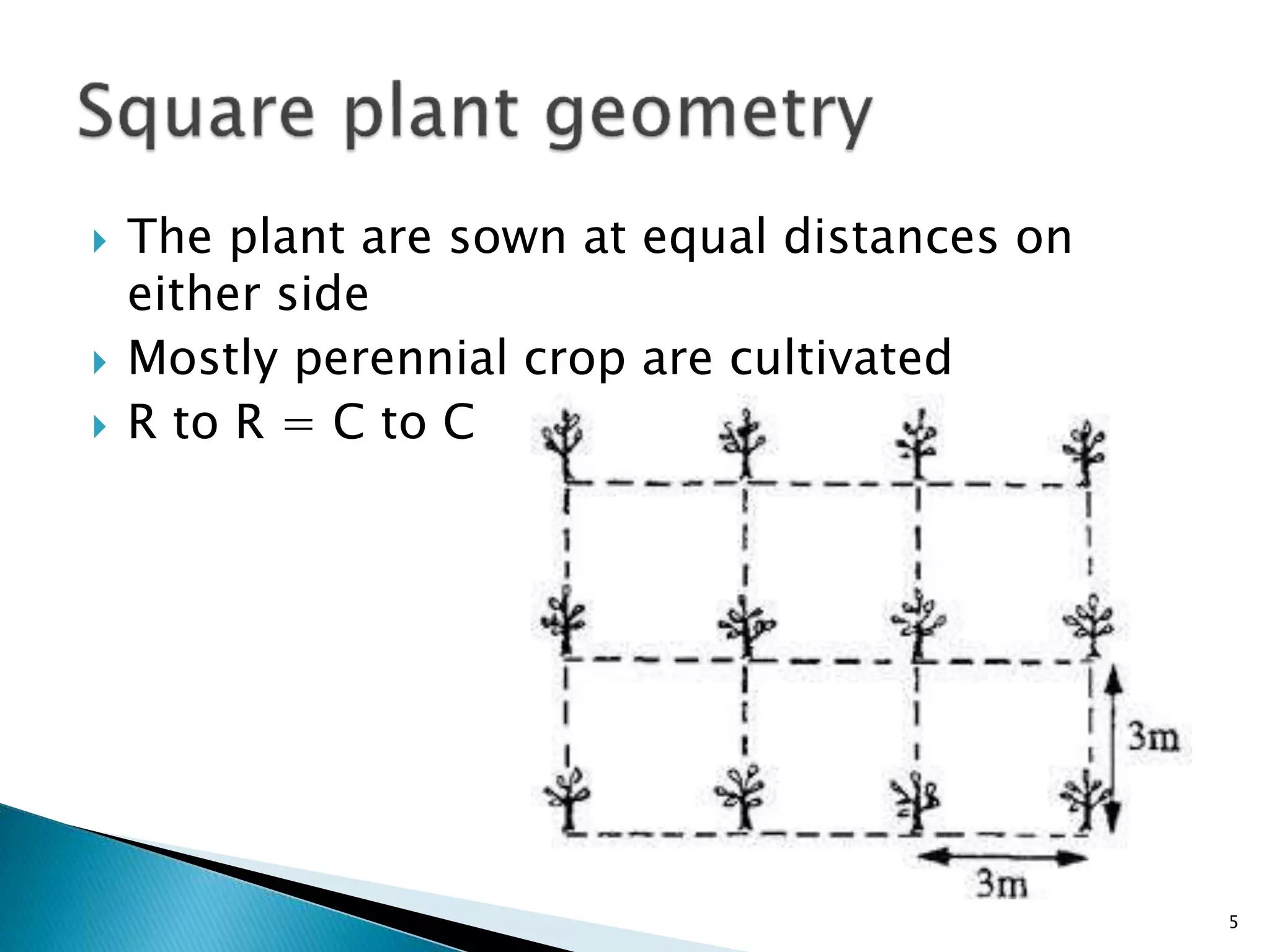
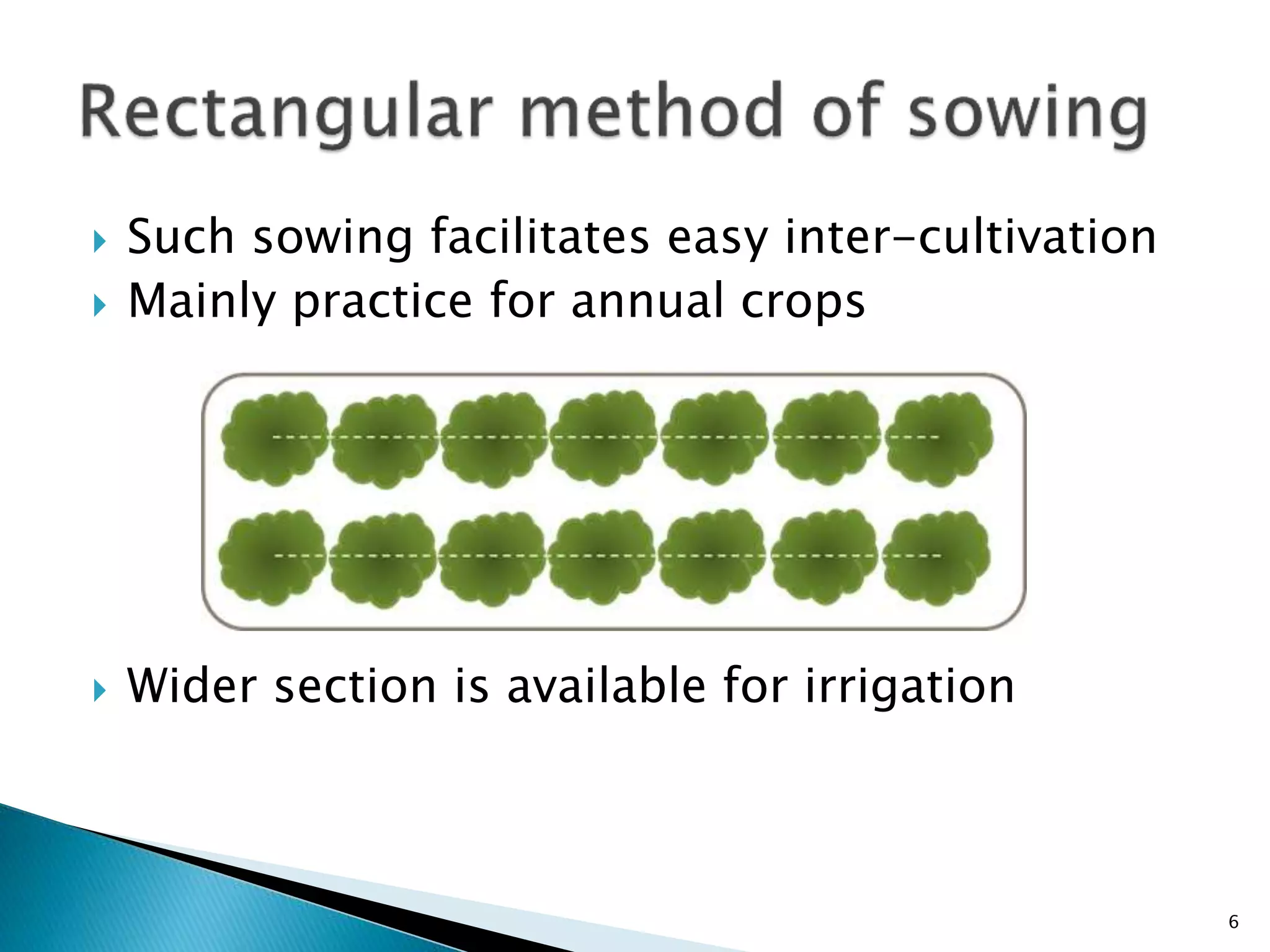


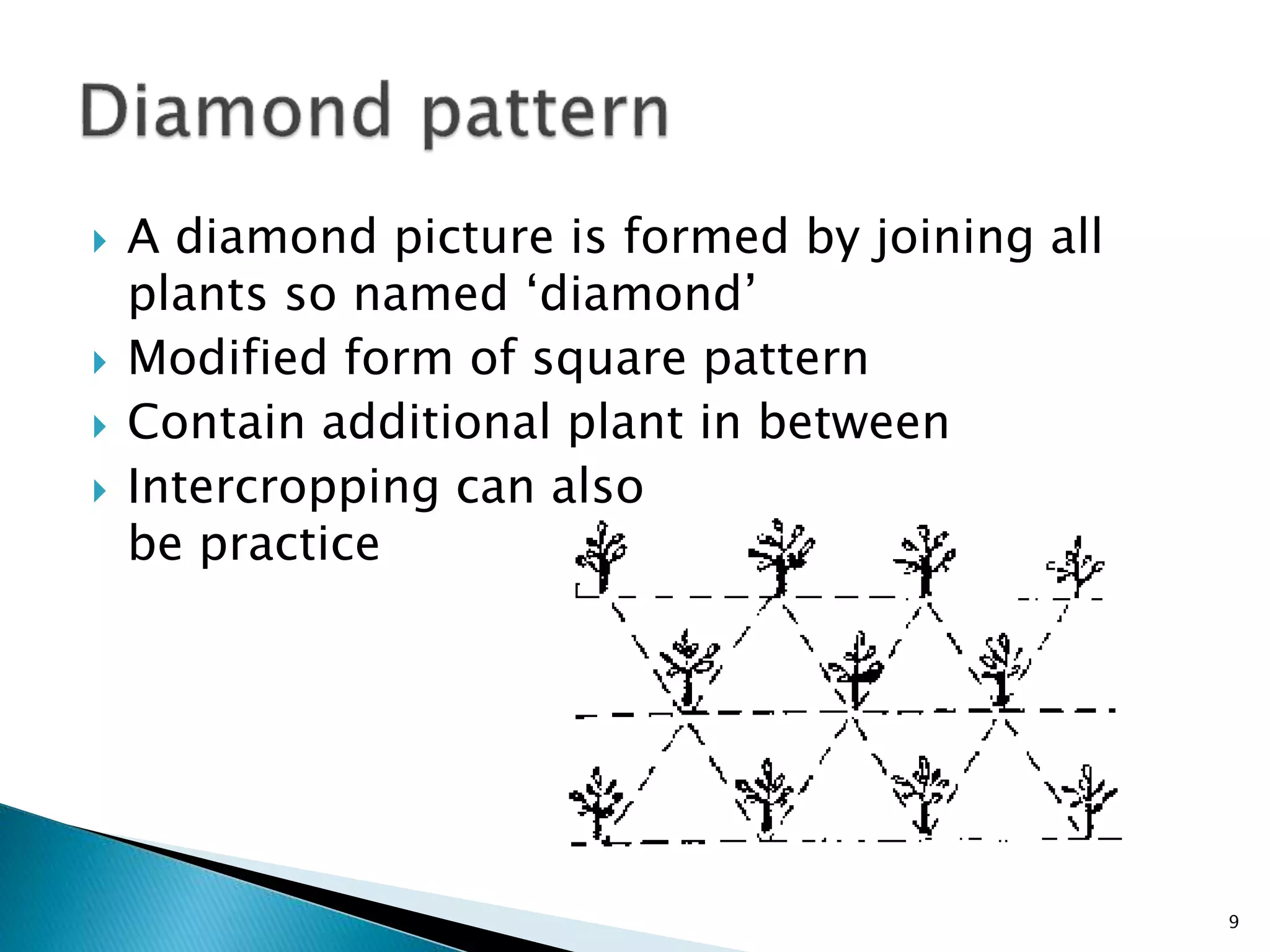


The document discusses various types of crop geometry and planting methods aimed at optimizing resource utilization. It covers arrangements such as square, rectangular, triangular, and diamond patterns, highlighting their advantages for different types of crops. Additionally, it provides specific plant populations and spacing for various crops to maximize yields.










