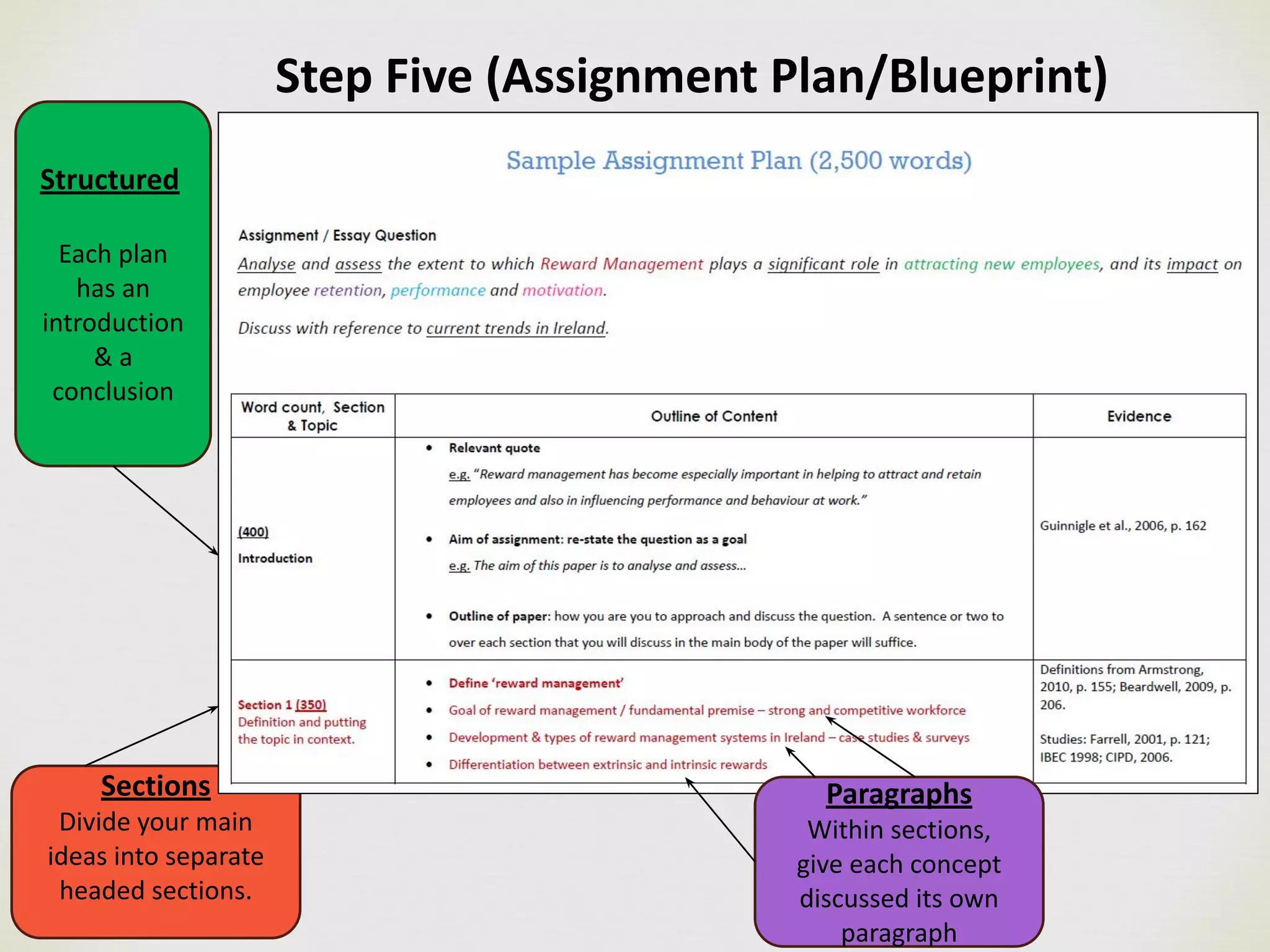
The document outlines a 6 step process for successfully planning and writing assignments: 1) Understand the assignment, 2) Get organized, 3) Conduct research, 4) Take and make notes, 5) Plan the structure, and 6) Write, reference, and proofread. Key aspects of each step are described, including analyzing the requirements, creating a schedule, using Boolean operators and synonyms in searches, paraphrasing sources, developing a blueprint with sections and paragraphs, writing drafts with evidence and citations, and editing for structure, references, and proofreading. Following these steps is presented as a way for students to produce high quality assignments with good sources, substance, structure, and style.