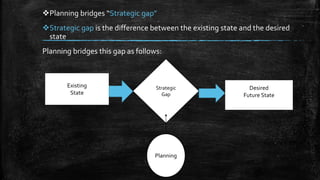
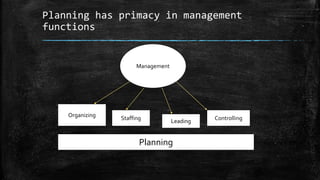
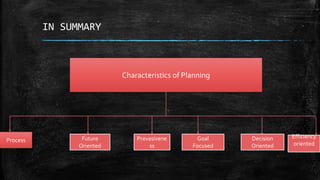
This document presents information on the concept of planning and its methods from a group presentation. It defines planning as setting goals and choosing actions to achieve them, and discusses its key characteristics as a process, future-oriented, prevasive, goal-focused, decision-oriented, and efficiency-oriented. The document also covers the importance of planning in reducing uncertainty, focusing goals, better coordination, efficiency promotion, environmental adaptation, and commitment. Finally, it discusses some limitations and different methods of planning including top-down, bottom-up, participative, and team methods.