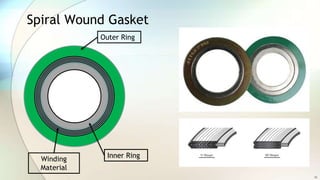
The document explains gaskets as sealing materials placed between flanges to create static seals and prevent leakage. It outlines selection criteria, types of gaskets including non-metal, metal, and composite varieties, along with their usage, advantages, and costs. Additionally, it promotes an online course for further learning about pipe and pipe fittings.