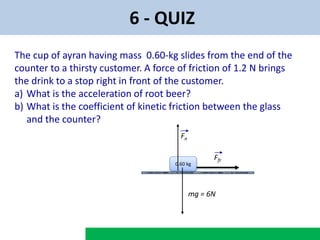
Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. If the net force on an object is zero, its velocity will be constant. The direction of the acceleration is always the same as the direction of the net force.