This document provides guidance on assessing the head and neck region during a physical examination. It begins by outlining the session objectives, which are to learn anatomy and physiology of the head and neck, components of the health history, specific examination techniques, normal findings, and documentation of significant findings.
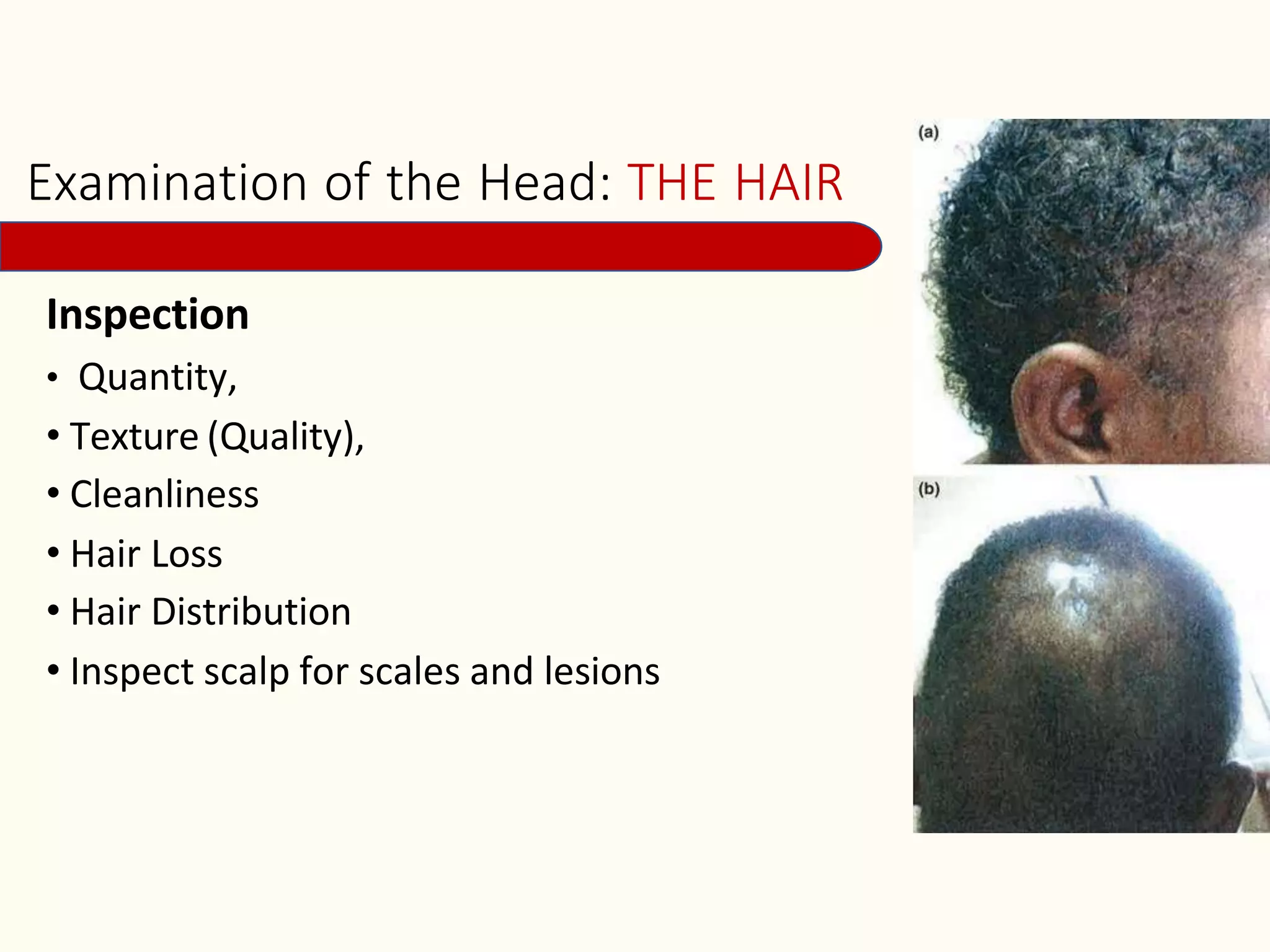
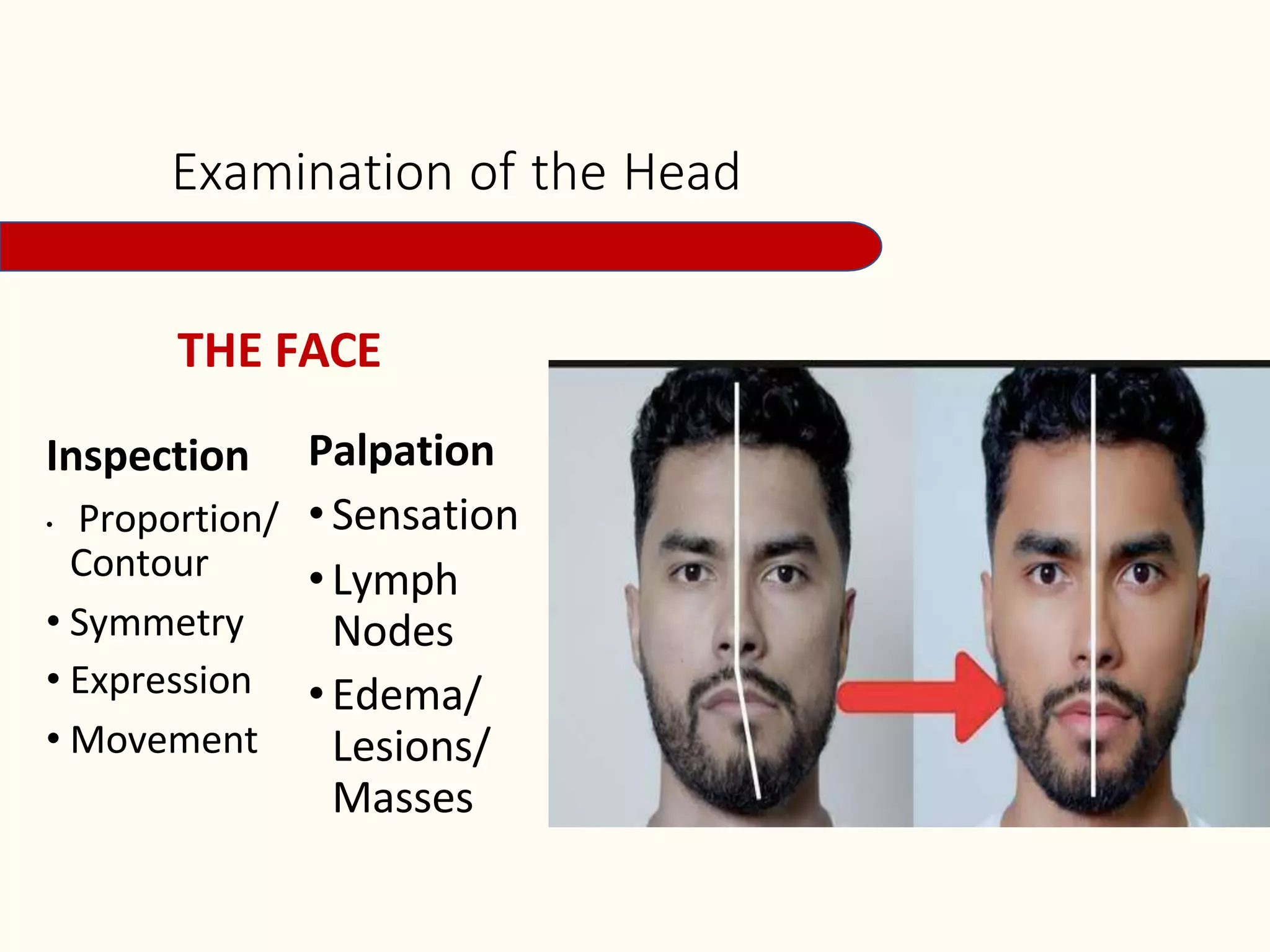
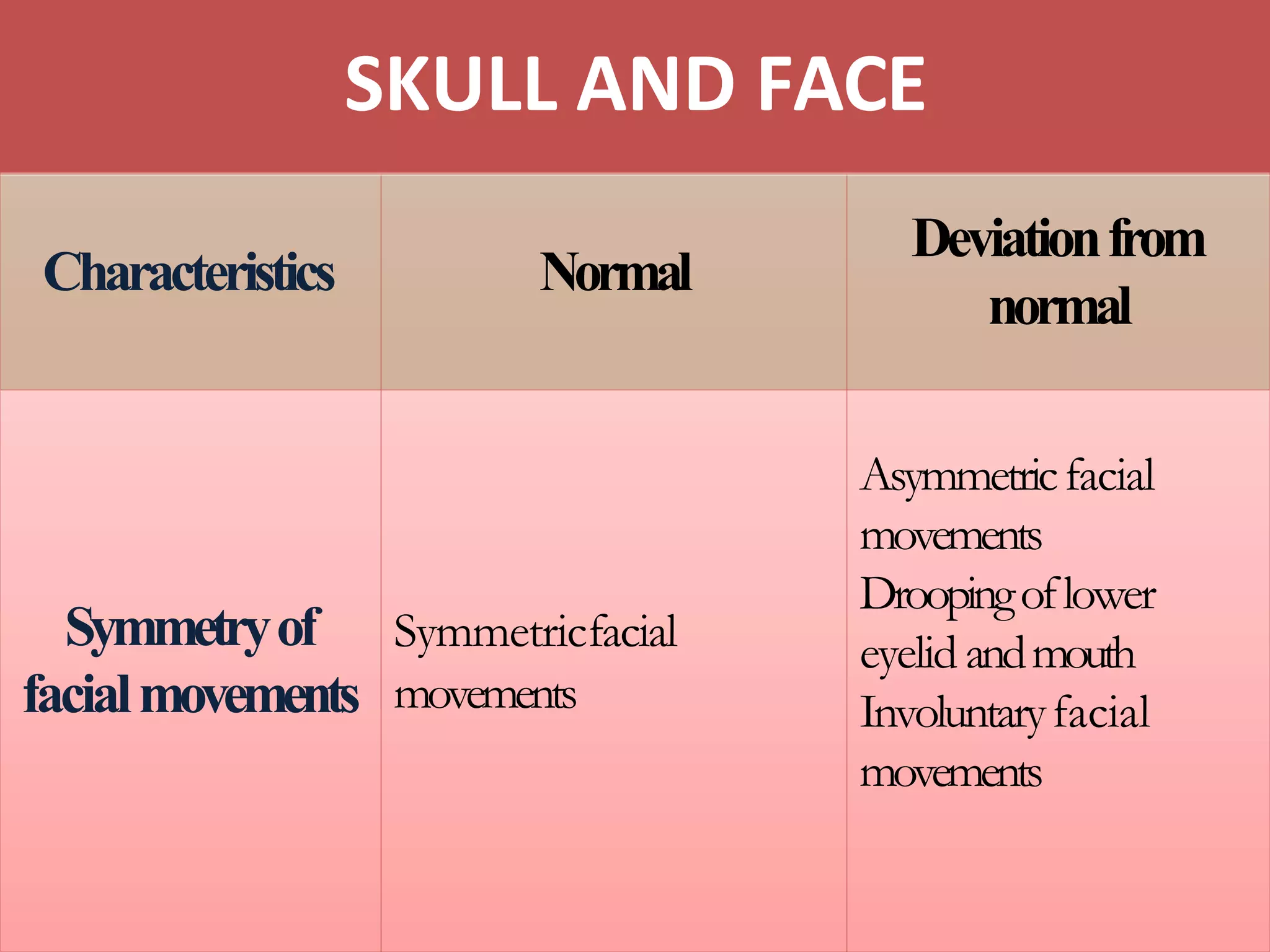
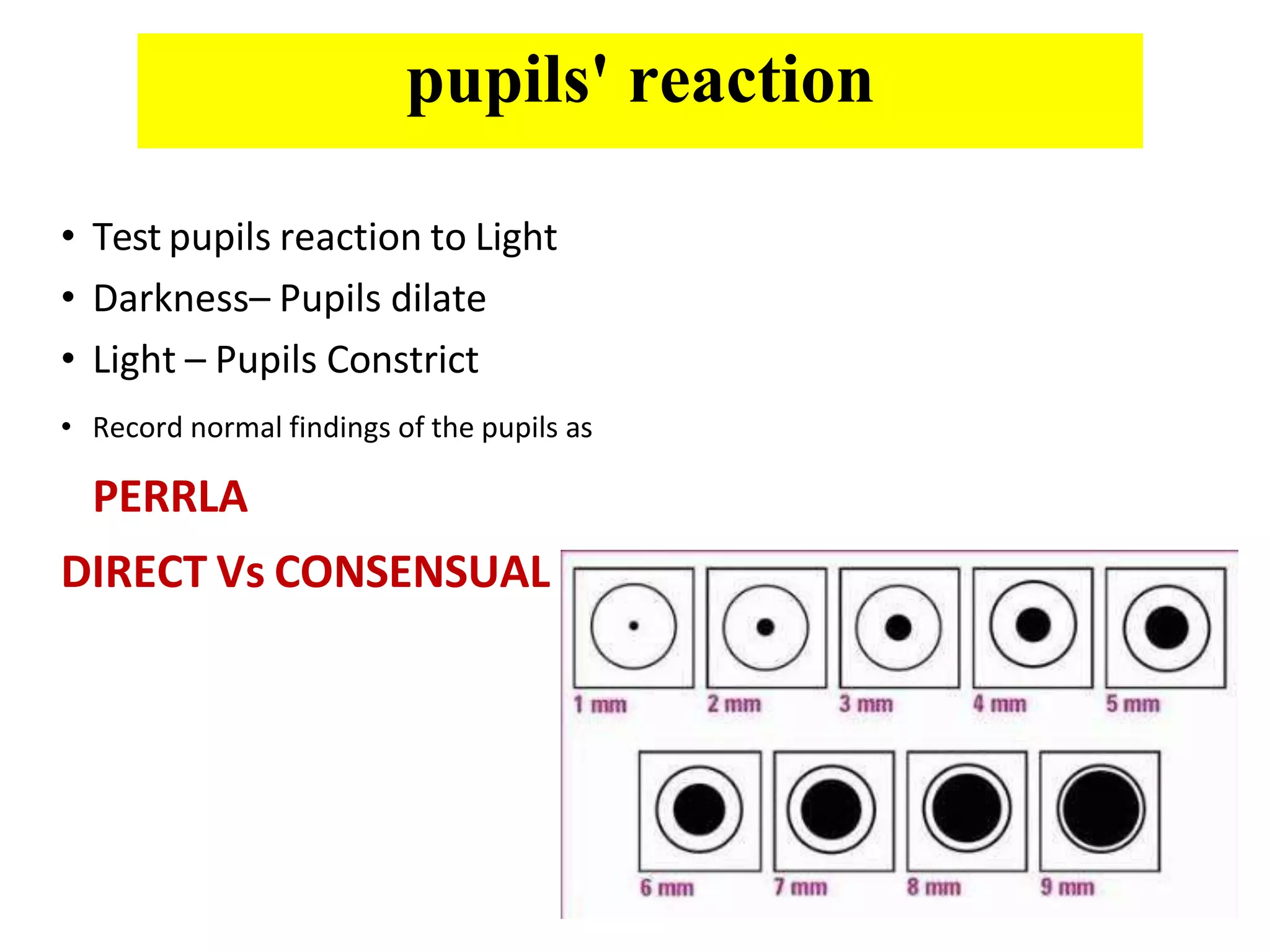
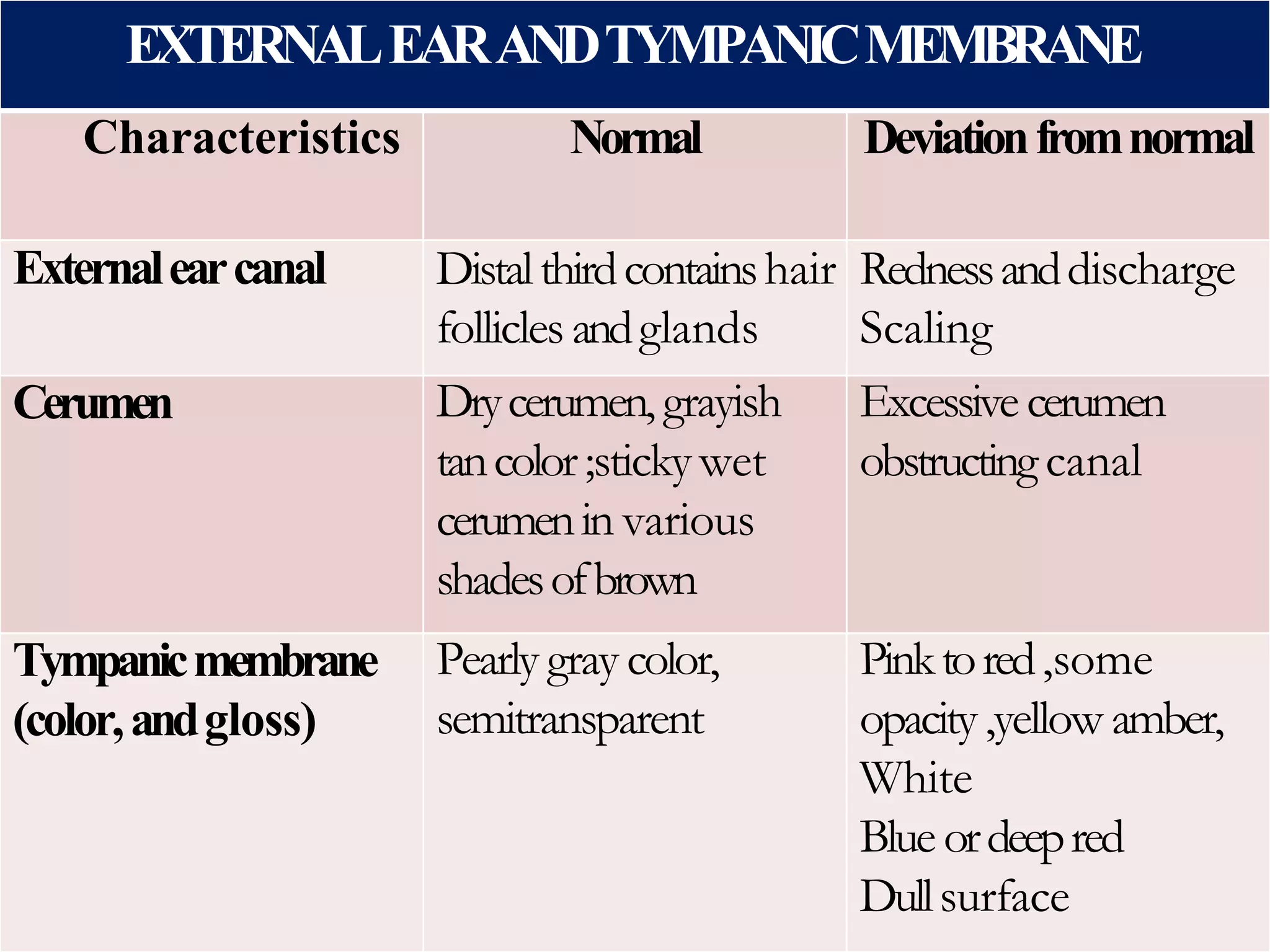
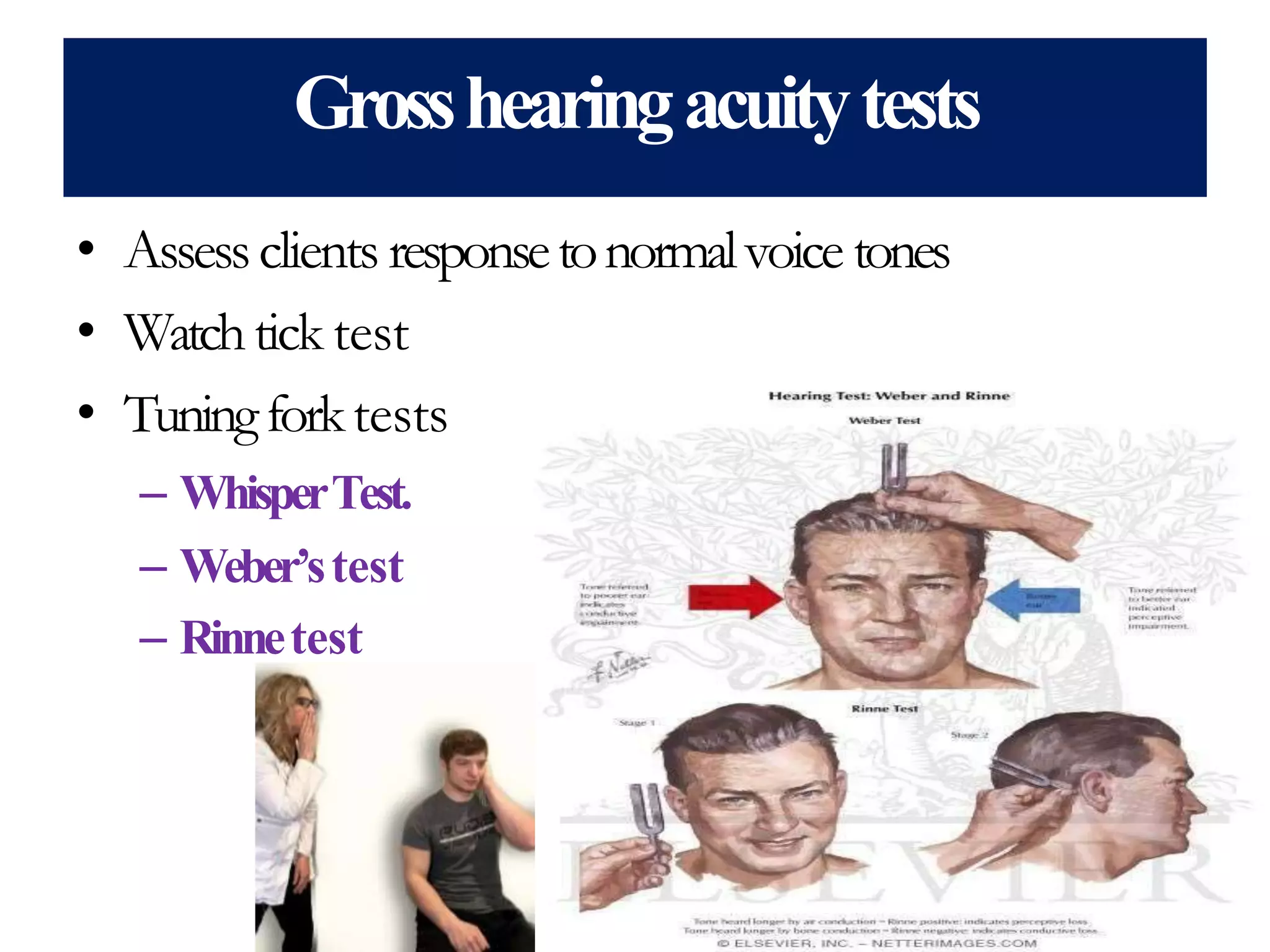
It then details the assessment of various head and neck structures including the skull, face, eyes, ears, nose, mouth, oropharynx and neck. For each area, it describes inspection, palpation and any specialized examination techniques, as well as normal findings and potential deviations. Standard protocols for the head and neck exam involving patient preparation, examination steps and possible history questions are also provided.