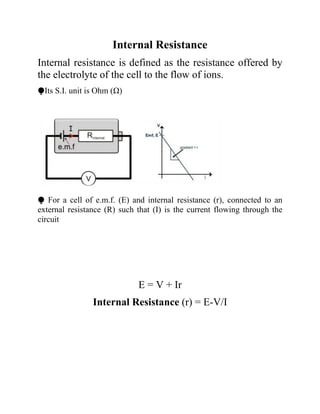
This project investigates the factors that affect the internal resistance of a cell. The student studies how internal resistance is impacted by the distance between electrodes, the surface area of electrodes in the electrolyte, the temperature of the electrolyte, and the concentration of the electrolyte. Experiments are conducted to determine the internal resistance of cells under different conditions for each of these factors. Observations are recorded and internal resistance values are calculated. The conclusion is that internal resistance increases with electrode separation and decreases with greater electrode area, higher electrolyte temperature, and higher electrolyte concentration.