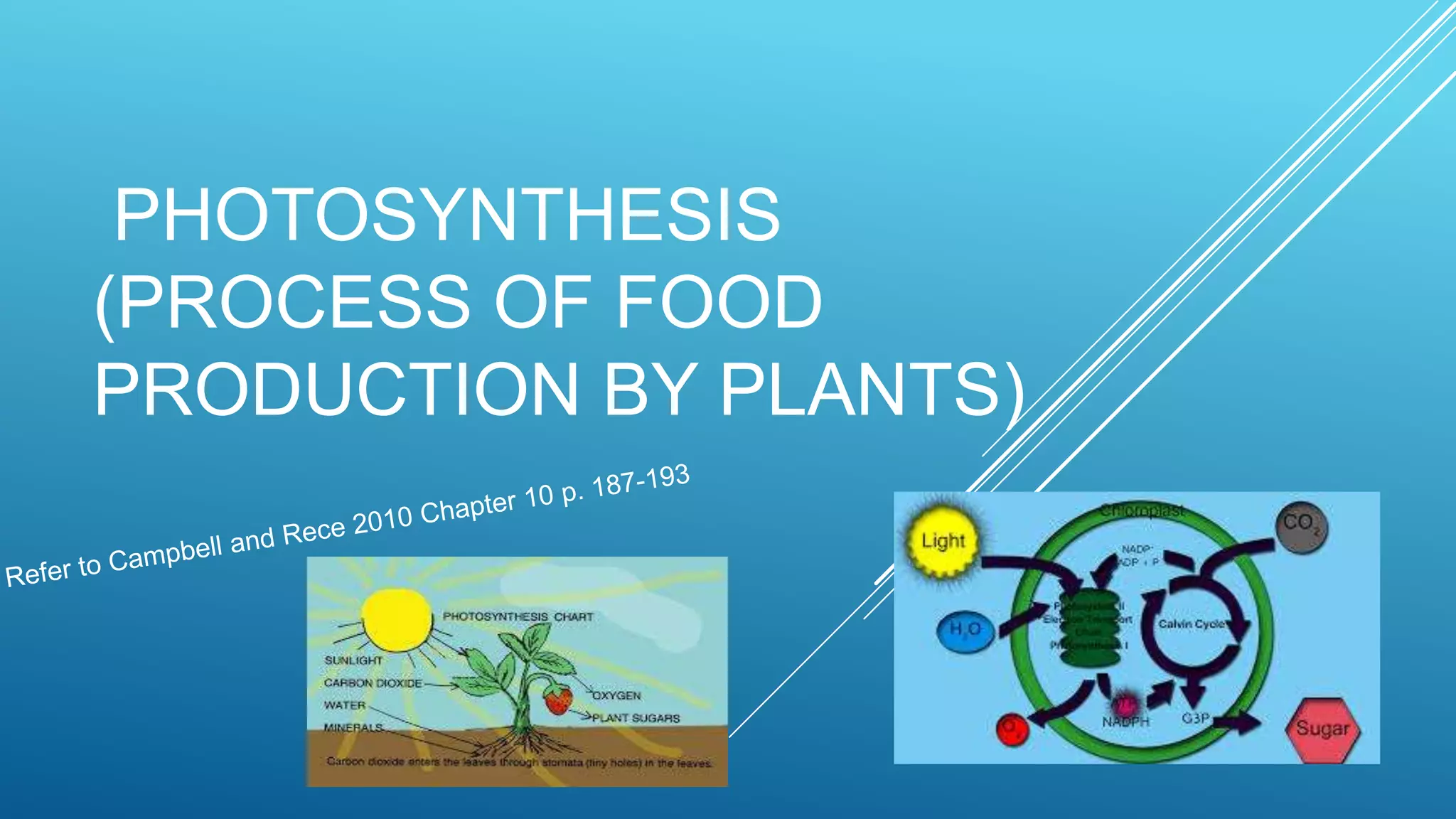
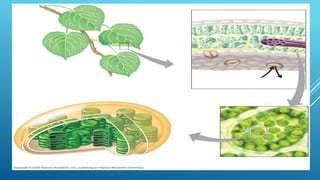
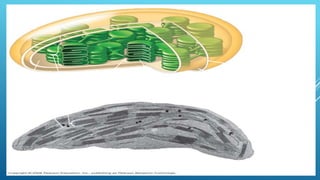
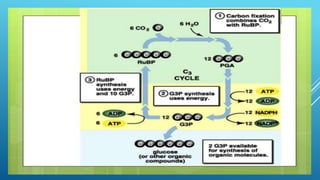
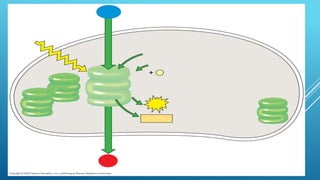
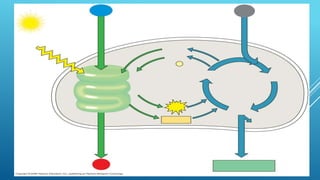
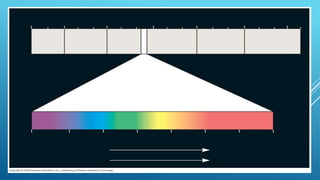
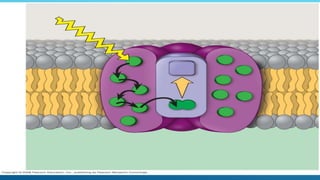
Green plants and other organisms perform photosynthesis, the process by which solar energy is converted into chemical energy and stored in organic molecules. During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight are used to produce glucose and oxygen. The two main stages are the light reaction phase, where light energy is absorbed and used to produce ATP and NADPH, and the Calvin cycle, where carbon dioxide is incorporated into organic compounds to form glucose. Chloroplasts in plant leaves contain chlorophyll which absorbs sunlight to drive photosynthesis, producing oxygen as a byproduct and fueling the biosynthesis of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats that sustain life on Earth.