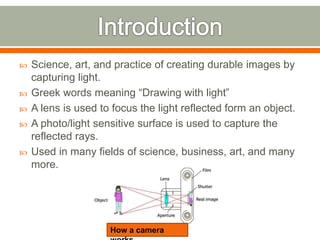
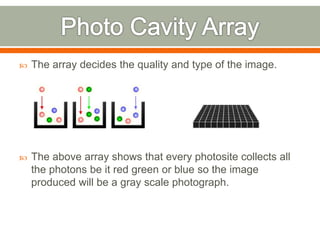
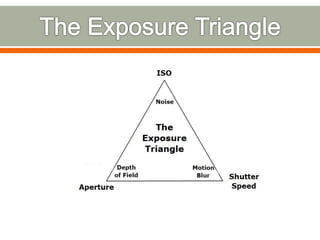
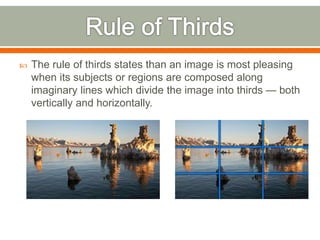
The document covers the fundamentals of photography, including its history, how cameras work, and various photography techniques. It discusses the evolution of photography from early inventions to digital technology and explains key concepts like exposure, composition, and image editing. Additionally, it highlights the importance of creativity and perspective in photography through various quotes and personal reflections.