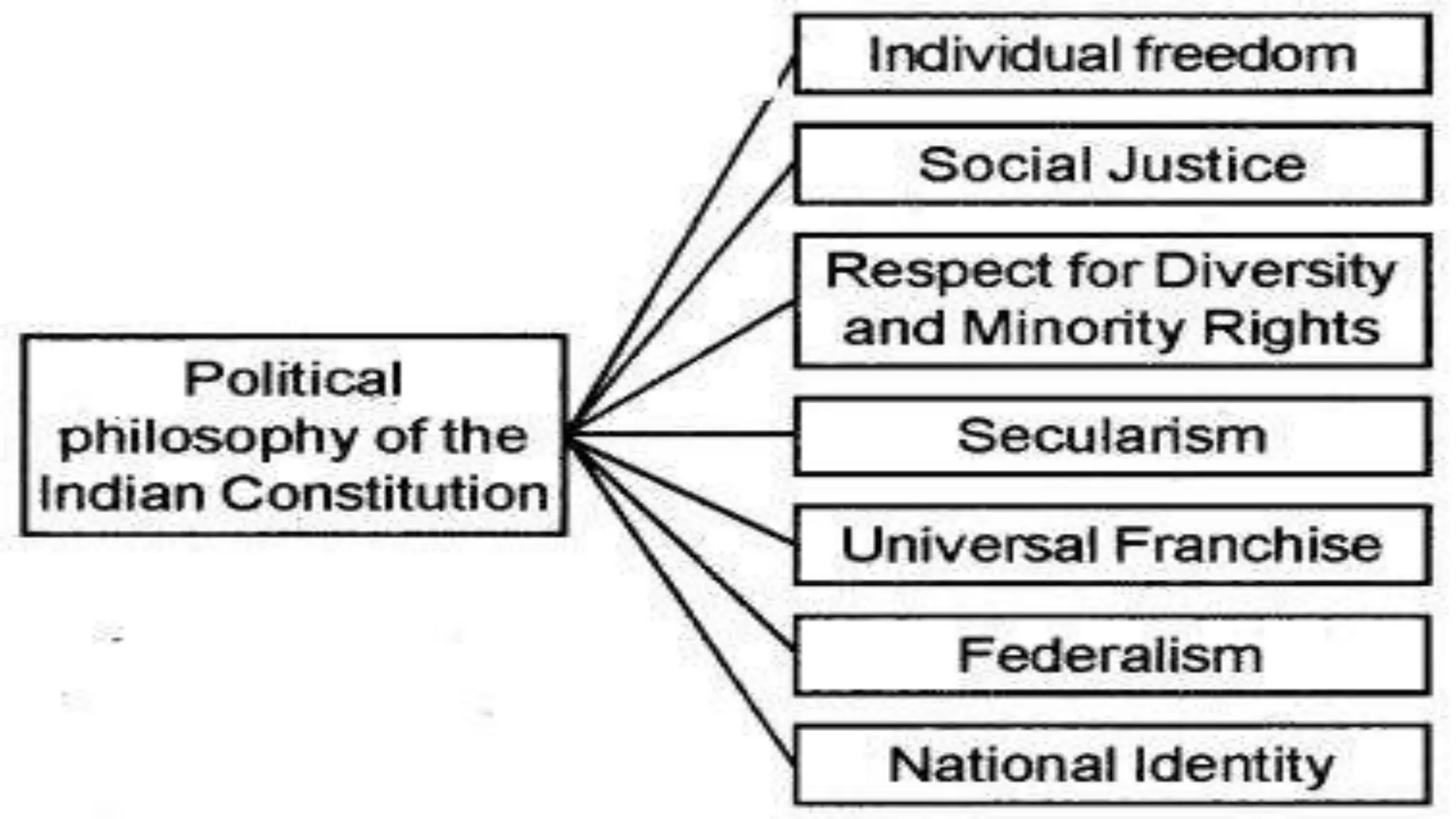
The document discusses the key philosophical principles that underlie the US Constitution: popular sovereignty, separation of powers, federalism, limited government, individual rights, and rule of law. It explains how each principle originated from political philosophers and how they are implemented and practiced through the Constitution and government. The concluding paragraph summarizes how these principles establish a democratic system and continue shaping American political life and democracy.