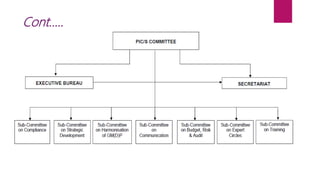
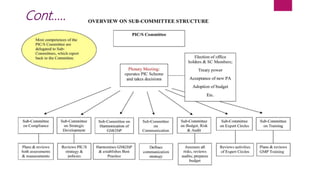
The Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme (PIC/S), established in 1995, is a non-binding arrangement aimed at harmonizing good manufacturing practices (GMP) among regulatory authorities worldwide. It facilitates training, international cooperation, and development of common standards, enhancing mutual confidence among its 53 member authorities. PIC/S operates through a flexible organizational structure and emphasizes consensus and networking to improve regulatory inspections and compliance in the pharmaceutical sector.