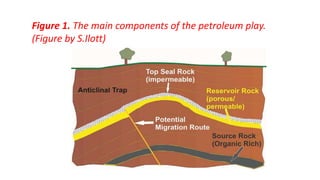
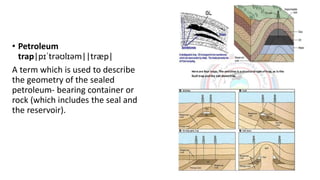
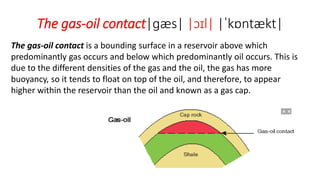
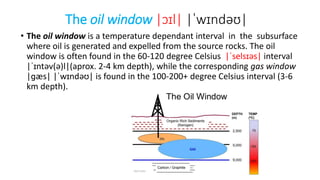
The document defines a petroleum play as a conceptual model that identifies locations where hydrocarbons may be found based on the combination of reservoir rocks, a source of hydrocarbons, sealing rocks, and a trap. The main components of a petroleum play are a source rock, migration pathway, reservoir rock, sealing rock, and trap. A petroleum play framework enables exploration for potential oil and gas deposits.