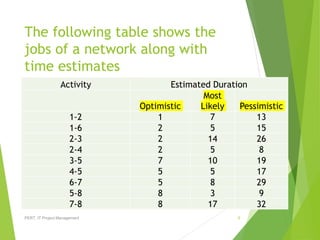
Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) is a network analysis technique used to estimate project duration when there is uncertainty about activity durations. PERT uses probabilistic time estimates based on optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic durations to account for risk. It involves developing schedules that are more realistic than critical path method (CPM) alone by considering multiple duration estimates for each activity. PERT can determine expected total time, activity start and end times, critical paths, how delays affect completion, and the probability of on-time completion.