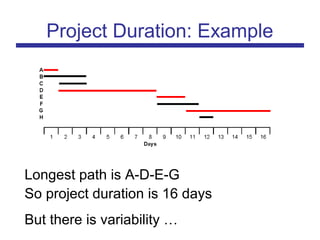
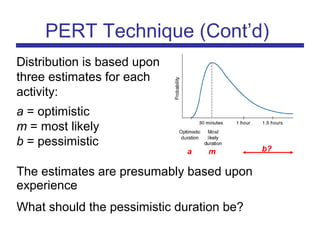
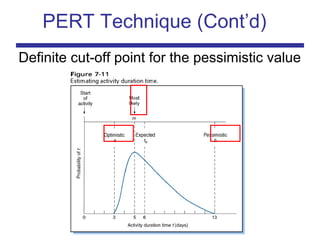
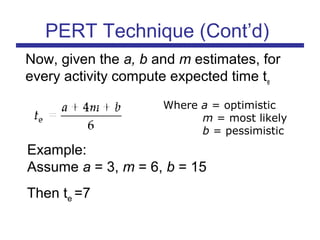
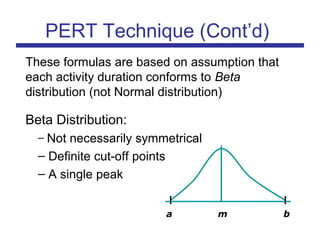
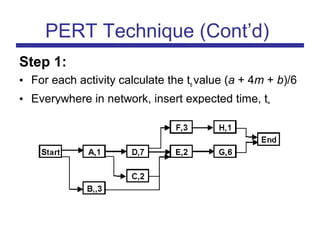
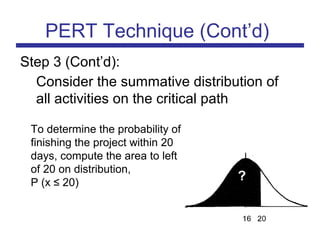
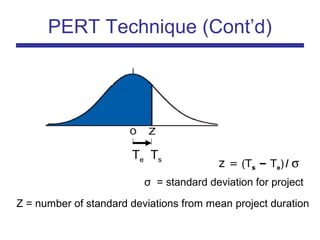
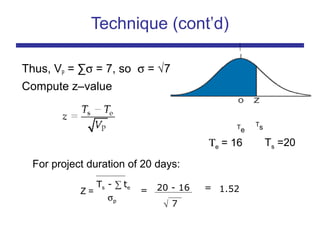
The document discusses the PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) method for addressing variability in activity durations and estimating project completion times probabilistically. PERT treats activity durations as distributions rather than fixed values. It uses three estimates (optimistic, most likely, pessimistic) for each activity to calculate the expected duration and standard deviation. The critical path is identified using expected durations. PERT then models the project duration as a normal distribution based on the sum of critical path activity distributions. This allows calculating the probability of completing within a given time frame, like the 93% probability of completing a project within 20 days as in the example.