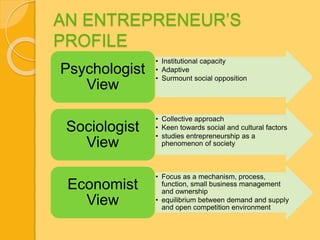
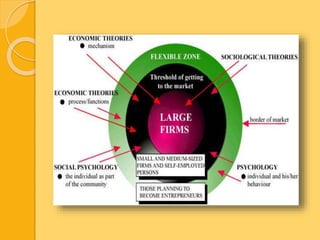
This document discusses entrepreneurship and innovation from different perspectives. It provides an overview of the personality and profile of entrepreneurs, discussing their traits from psychological, sociological, and economic views. Various theories of entrepreneurship are explained, along with the link between innovation and entrepreneurship. The document emphasizes that innovation can create new resources or increase the value of existing resources. It outlines strategies for innovation and discusses sources of innovation within and outside a company. These may come from unexpected occurrences, incongruities, changes in demographics or perception.