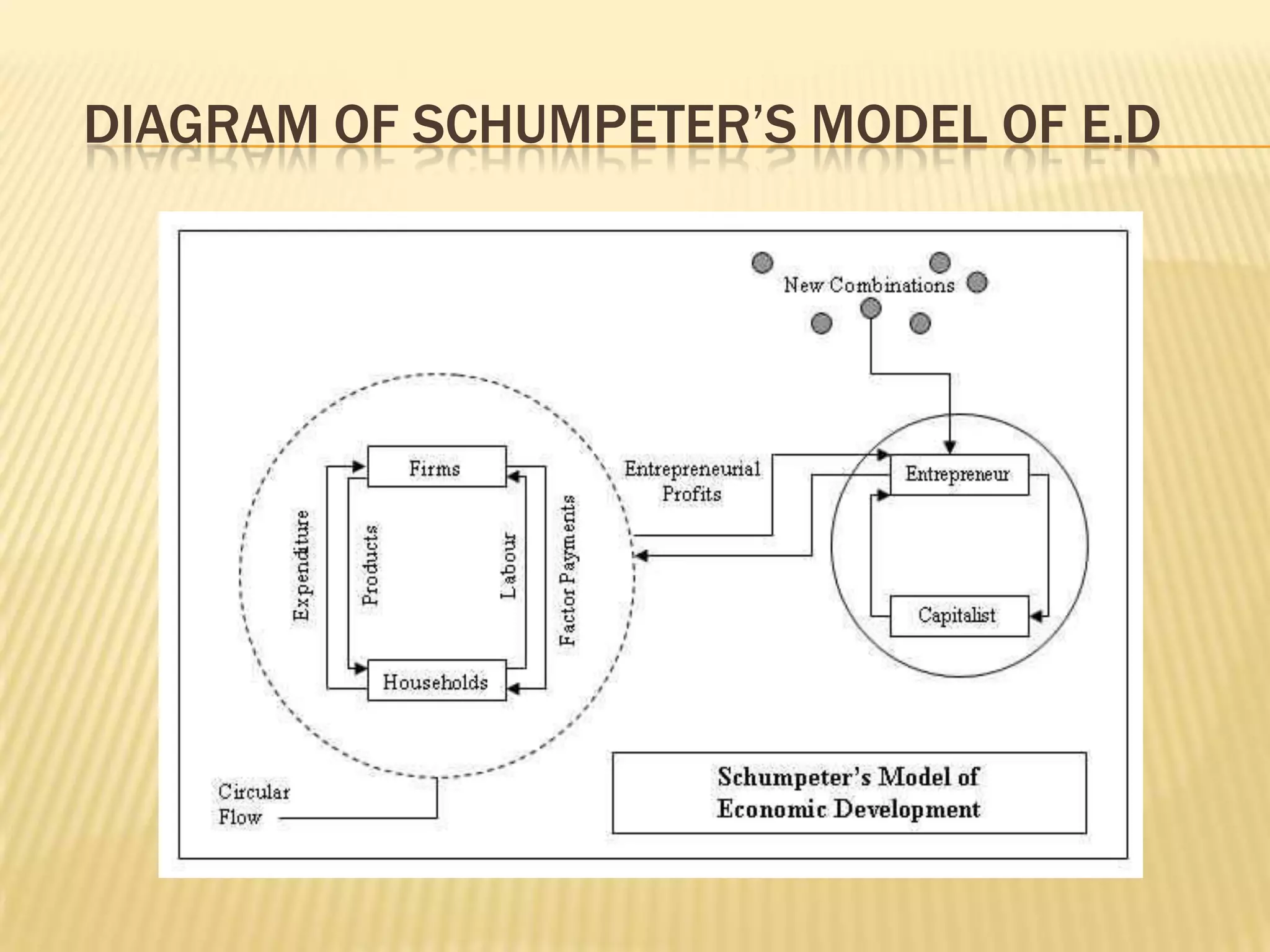
1. Schumpeter's model of economic development assumes a stationary economy in equilibrium that is disrupted by innovations introduced by entrepreneurs.
2. Entrepreneurs obtain credit from banks to implement innovations in the form of new products or production methods, breaking the circular flow and generating profits.
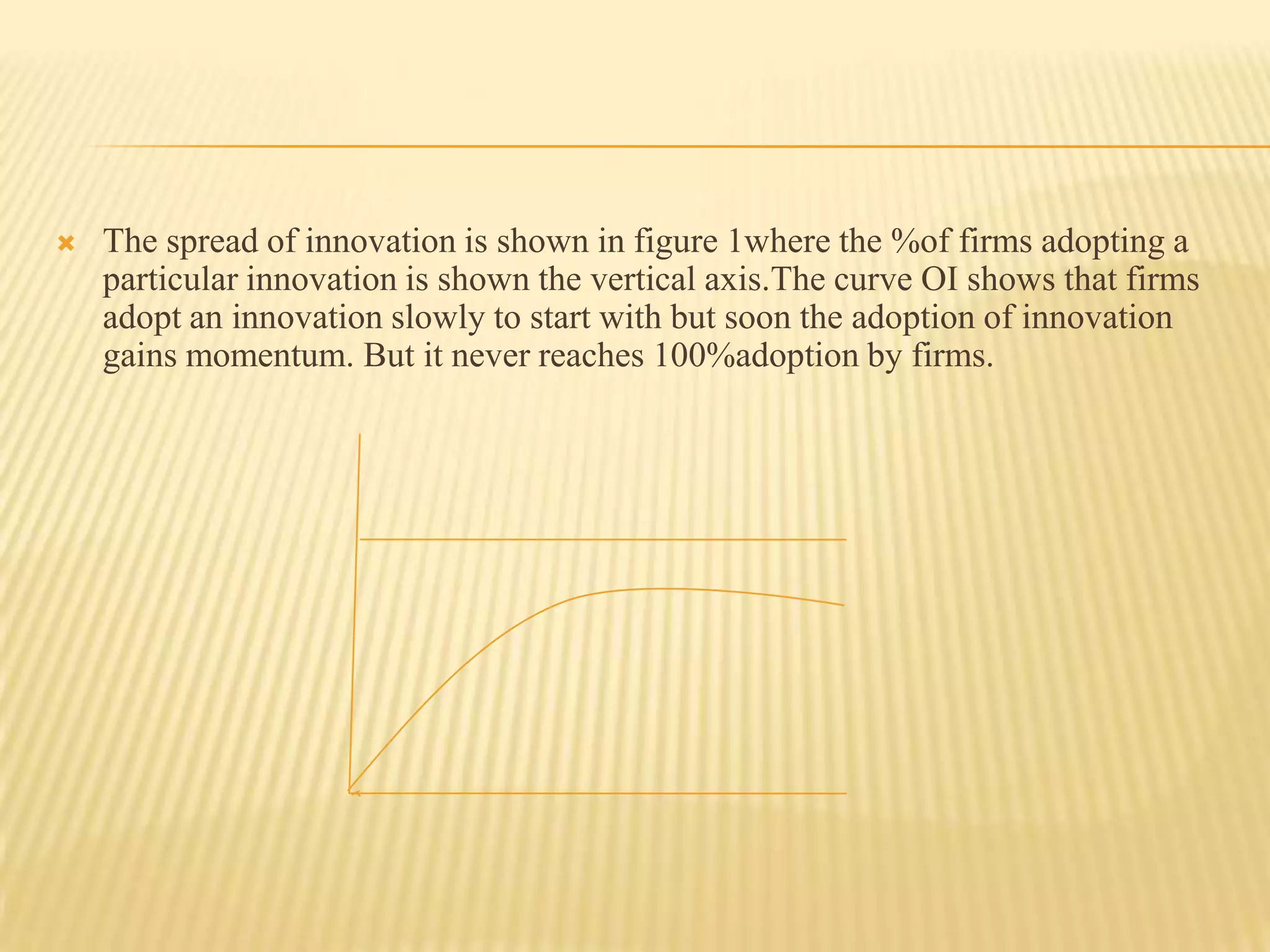
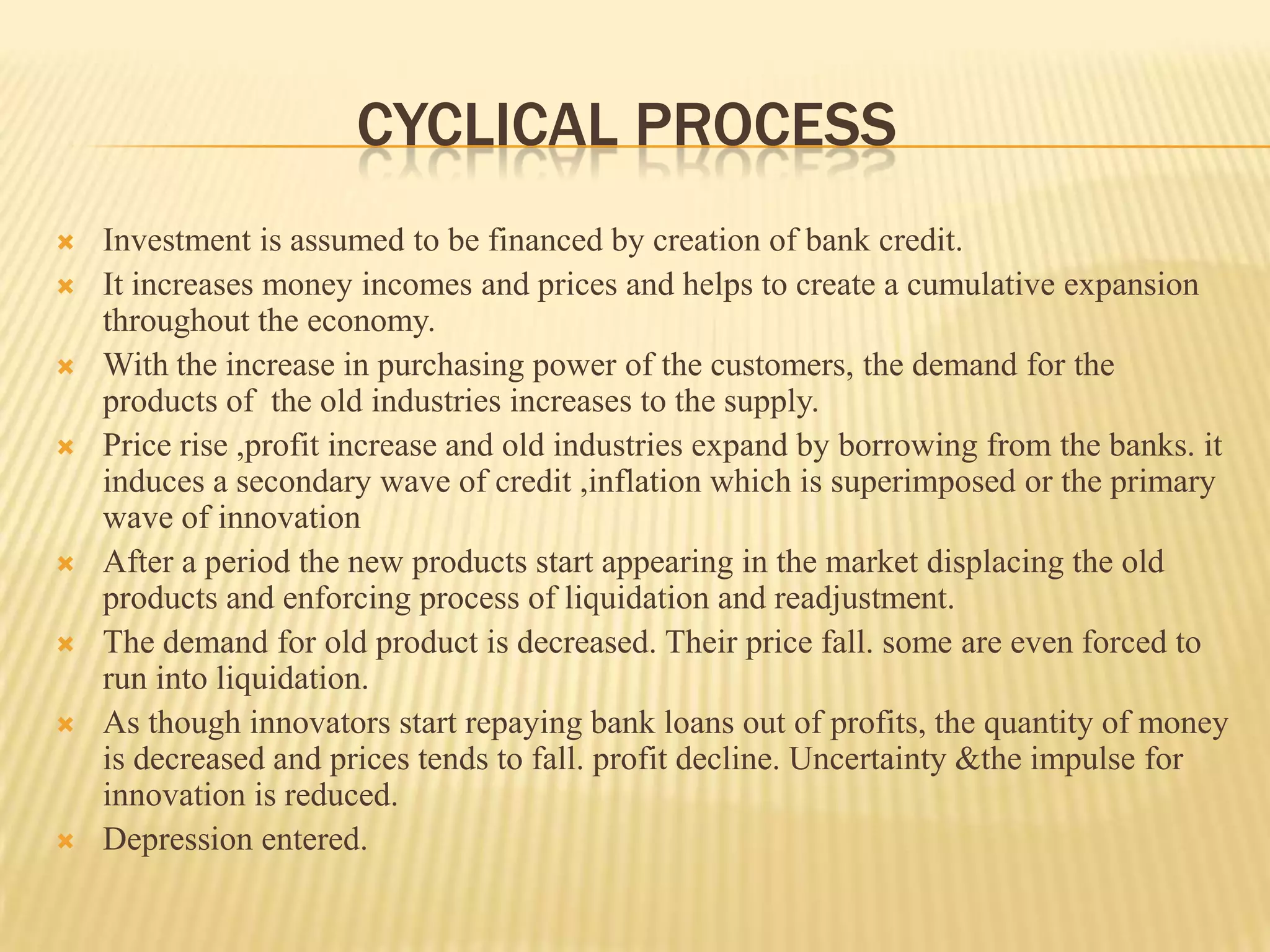
3. Successful innovations are then adopted by other firms, creating secondary effects that lead to inflation, an economic boom, and eventual recession as the innovations diffuse fully through the economy.