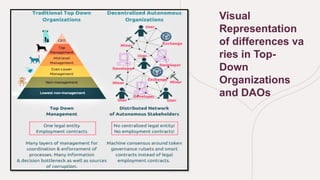
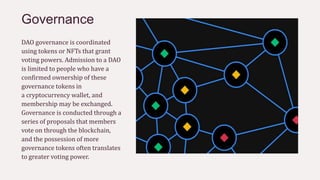
A decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) operates as a member-owned community governed by rules encoded on a blockchain, eliminating the need for centralized leadership. Members use governance tokens for voting, but face challenges like unlimited liability and a lack of consistent regulatory frameworks. As this model evolves, it promises to disrupt traditional organizational structures and improve efficiency across various sectors.