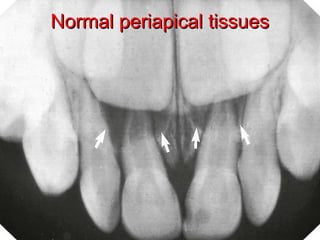
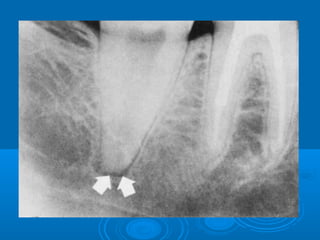
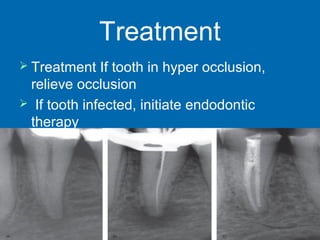
This document discusses different types of periapical lesions. Normal periapical tissues show no pain or sensitivity, have an intact lamina dura, and normal periodontal ligament. Symptomatic apical periodontitis is a painful inflammation of the periodontium through the root canal that can result from trauma, irritation, or infection, regardless of whether the tooth is vital or non-vital. Asymptomatic apical lesions are clinically asymptomatic conditions of pulpal origin that involve inflammation and destruction of periapical tissues. They result from pulp necrosis and can be detected through negative vitality tests, slight sensitivity to palpation, interruptions in the lamina dura on radiographs, and destruction of periapical