The document discusses mandibular fractures, including:
1. Mandibular fractures occur more frequently than other facial bone fractures and can be encountered by dental surgeons. They are broadly divided into fractures with or without bone communition and soft tissue loss.
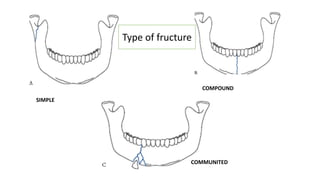
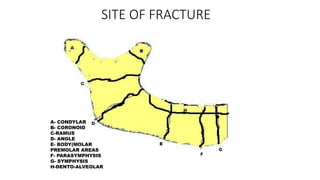
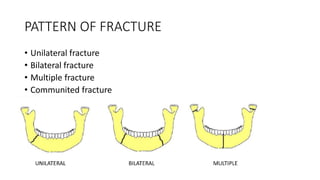
2. Fractures are classified by type (simple, compound, communited, pathological), site (condylar, coronoid, ramus, etc.), and cause (direct violence, indirect violence, muscle contraction).
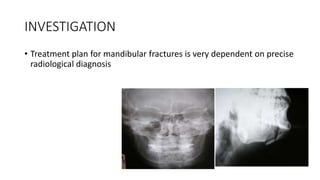
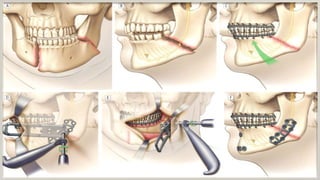
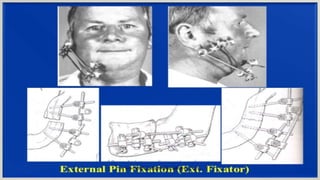
3. Signs and symptoms include swelling, pain, drooling, and limitations in mouth opening. Precise radiological diagnosis is needed to determine the treatment plan, which involves medical therapy with antibiotics and surgical fixation of the bone until stable.