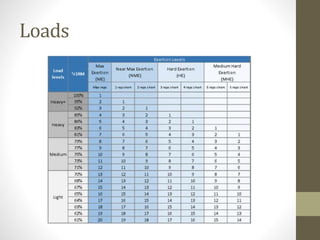
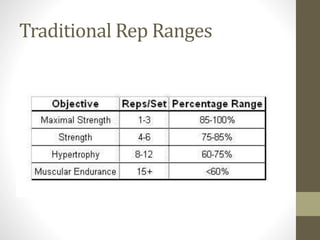
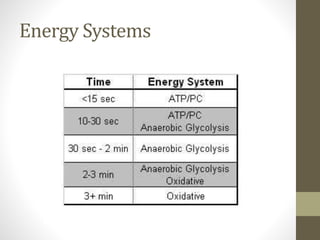
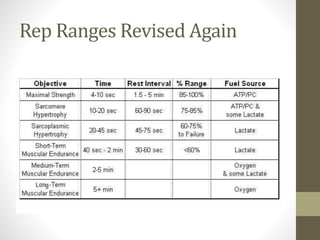
This document discusses various concepts related to developing effective training programs, including:
- Targeting different muscle groups on different days can be effective for muscle mass but not optimal for performance. The best approach depends on one's goals.
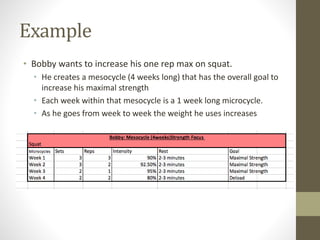
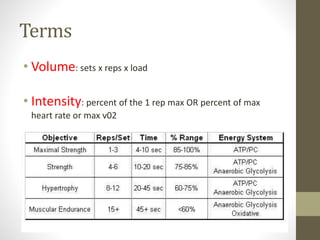
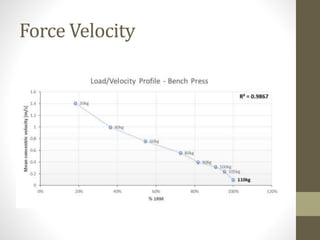
- Training programs should include goals, methods, individual session plans, and progression over time. Progressive overload via increased intensity, duration, or volume over time is important.
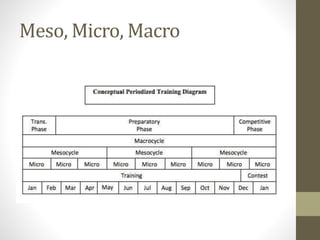
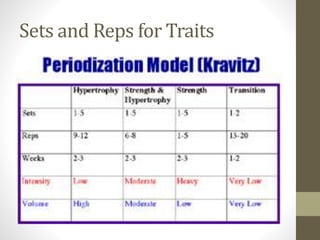
- Periodization involves planned training sessions over months or years to develop specific fitness traits and achieve goals. Micro, meso, and macrocycles group sessions at different timescales.
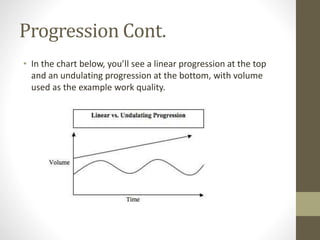
- Programs can use linear, undulating, or other models to progressively manipulate volume and intensity over time in different ways to optimize