Embed presentation


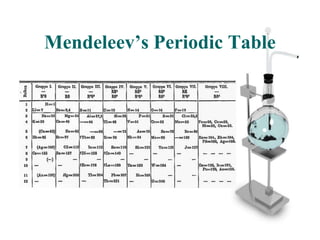

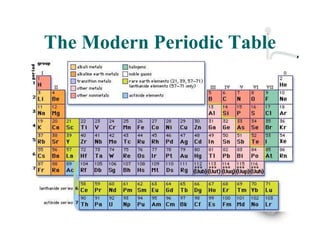
Glenn Seaborg discovered the transuranium elements from 94 to 102 in the mid-20th century and reconfigured the periodic table by placing the actinide series below the lanthanide series. He was awarded the 1951 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work, and element 106 was named seaborgium in his honor. The modern periodic table arranges elements in order of increasing atomic number, with rows called periods and columns called groups.




