Embed presentation

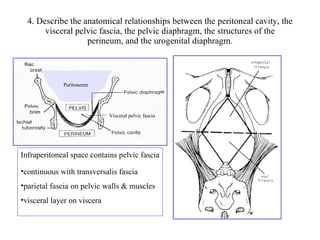






The document discusses pelvic anatomy related to innervation of pelvic organs, relationships between pelvic structures, the rectum and anal sphincters, and male and female sexual function. Key structures mentioned include the inferior and superior hypogastric plexus, peritoneum, pelvic fascia, pelvic diaphragm, levator ani muscle, pudendal nerve, internal pudendal artery, bulbospongiosus muscle, ischiocavernosus muscle, and vasculature of the penis and clitoris.






