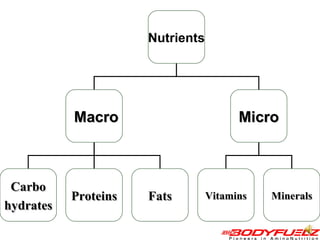
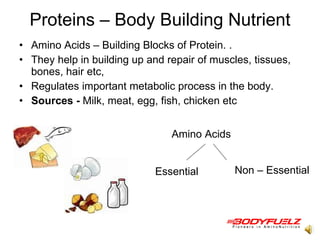
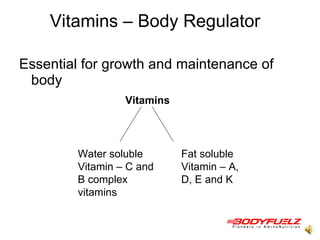
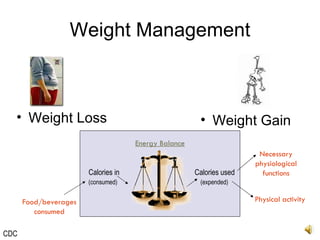
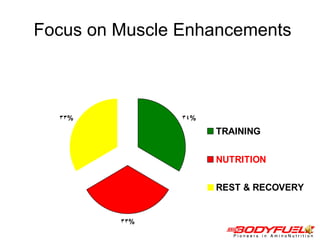
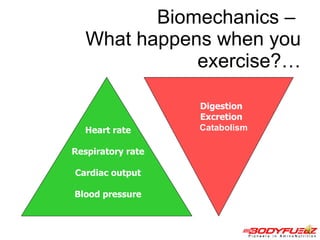
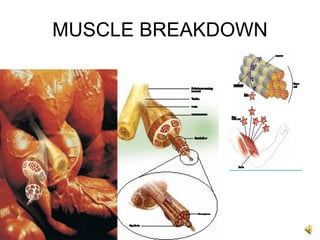
The document discusses balanced nutrition and macronutrients needed for performance and muscle building. It provides details on carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. It also discusses calculating basal metabolic rate and daily calorie needs. The key aspects are a balanced diet containing the right proportions of macros, sufficient calories for goals, and proper recovery nutrition including protein and amino acids to prevent muscle breakdown.