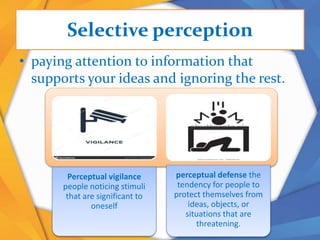
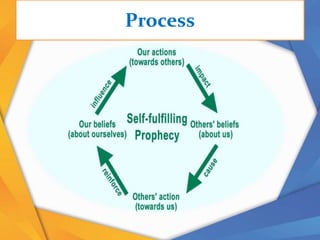
This document discusses several perceptual biases that can influence how people perceive and make judgments about others and situations. It describes the fundamental attribution error, where people underestimate external influences and overestimate internal influences in judging others. It also discusses biases like the halo effect, horn effect, similar-to-me effect, selective perception, perceptual vigilance, first impressions error, self-fulfilling prophecy, and stereotypes. These perceptual biases can negatively impact organizations through effects on job appraisals, promotions, team dynamics, and employee motivation levels.