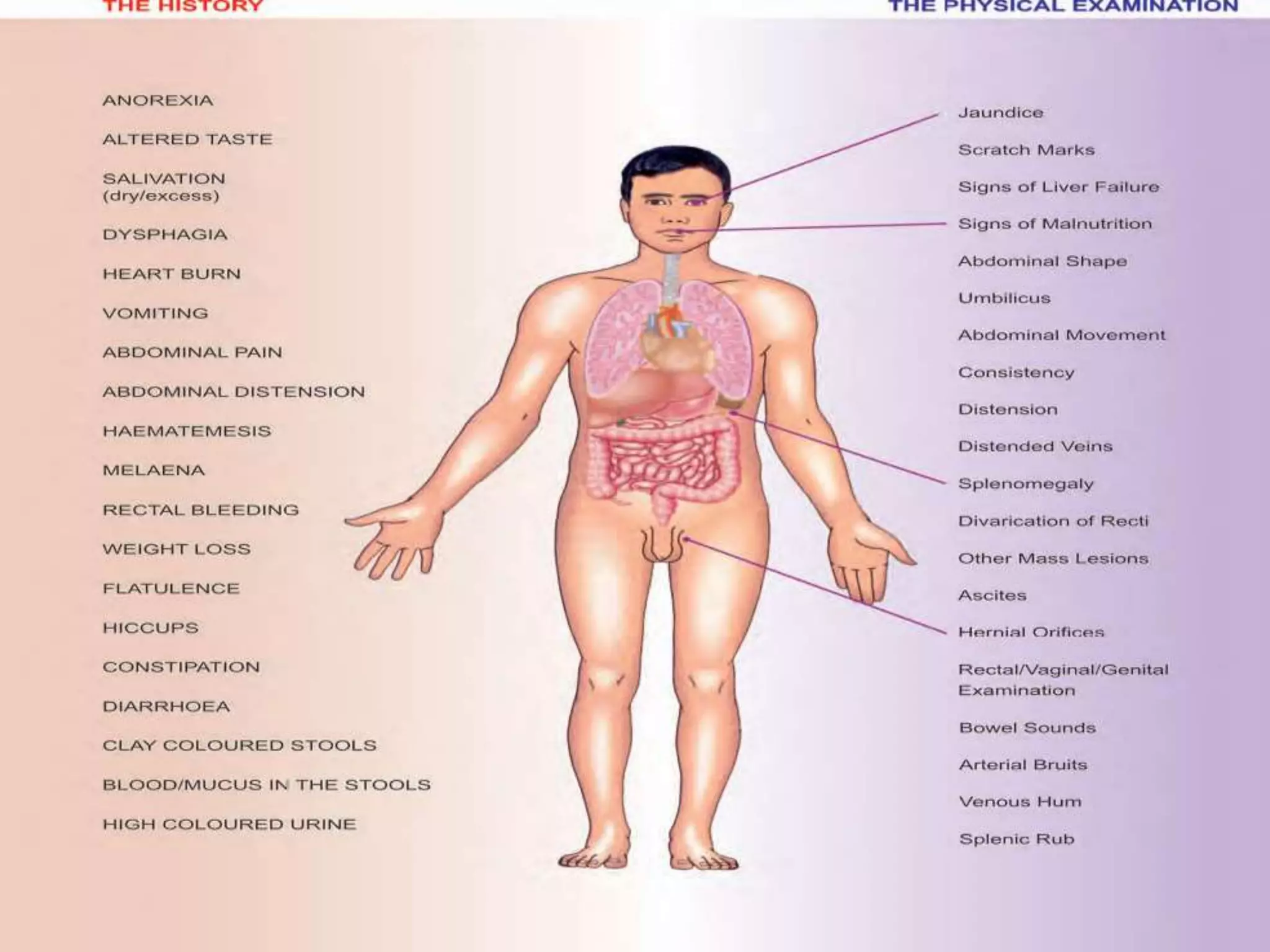
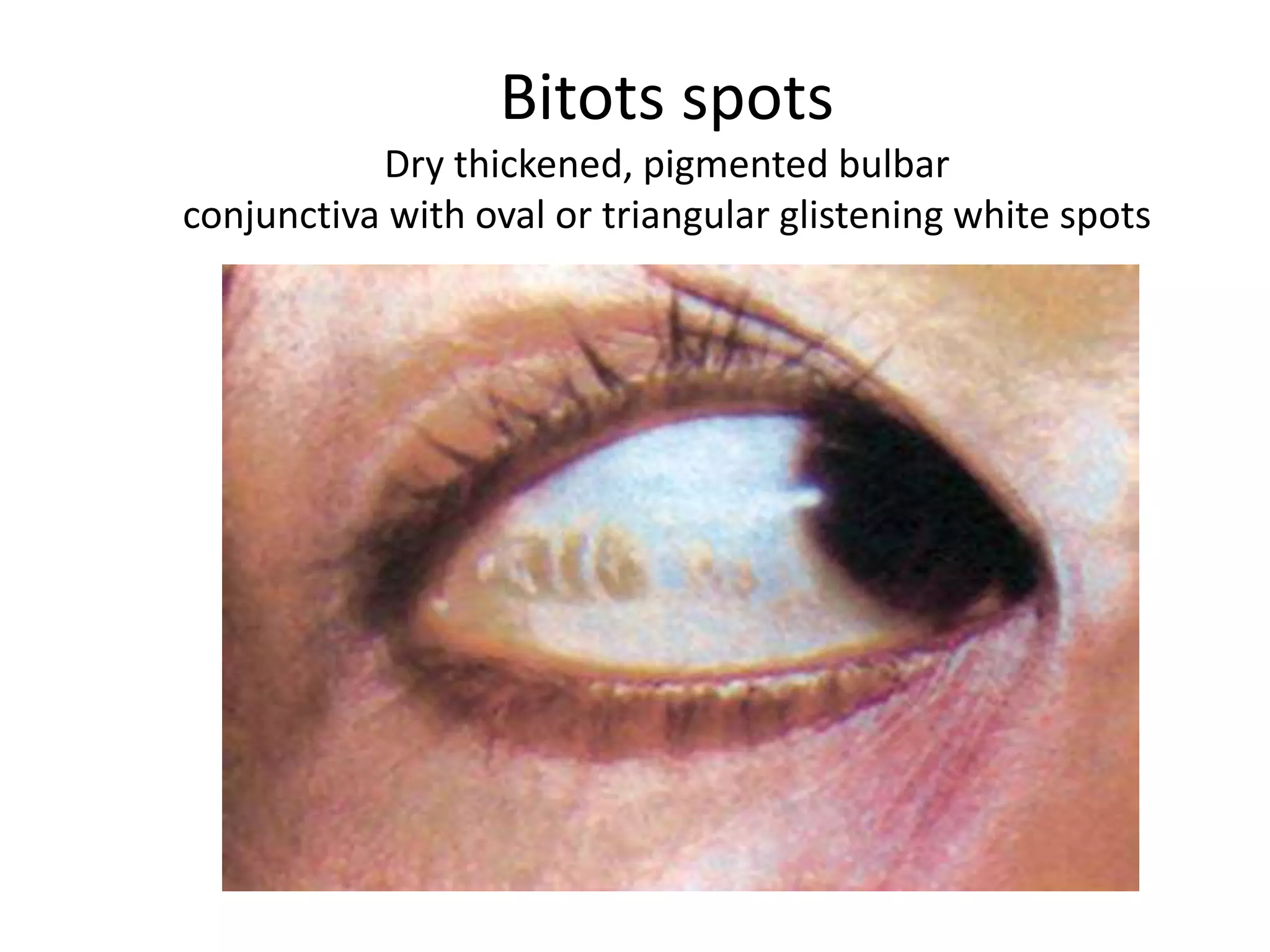
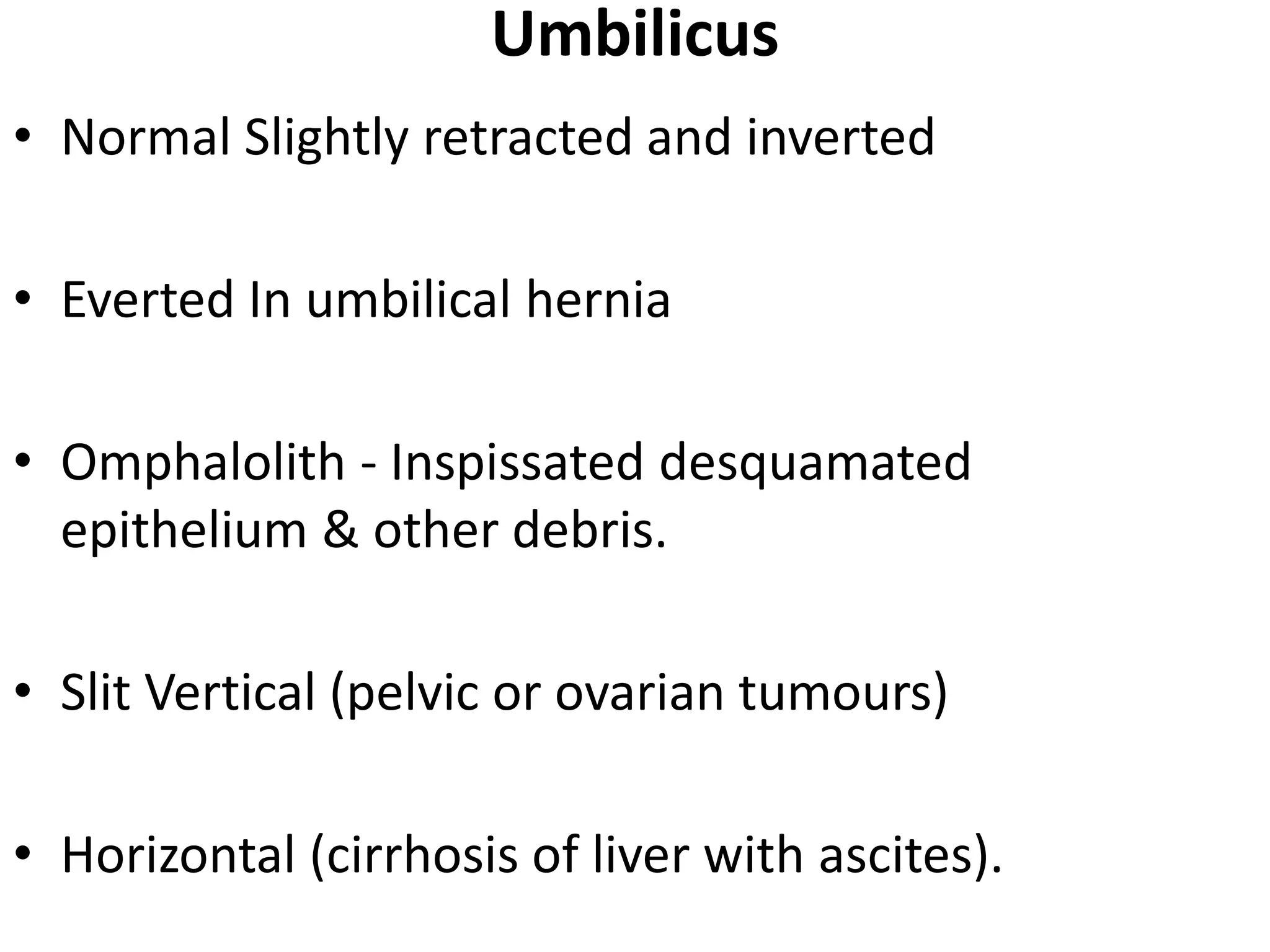
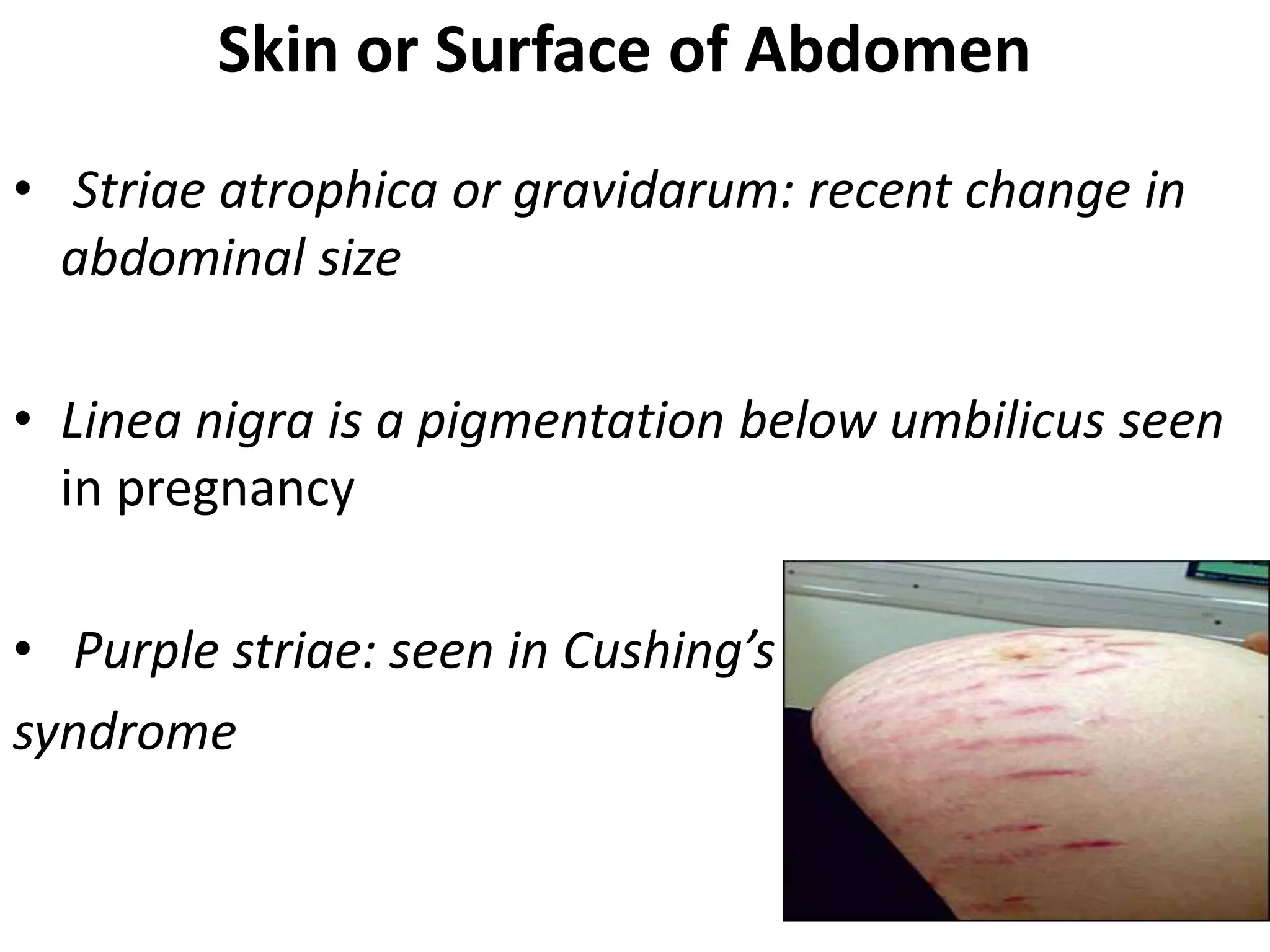
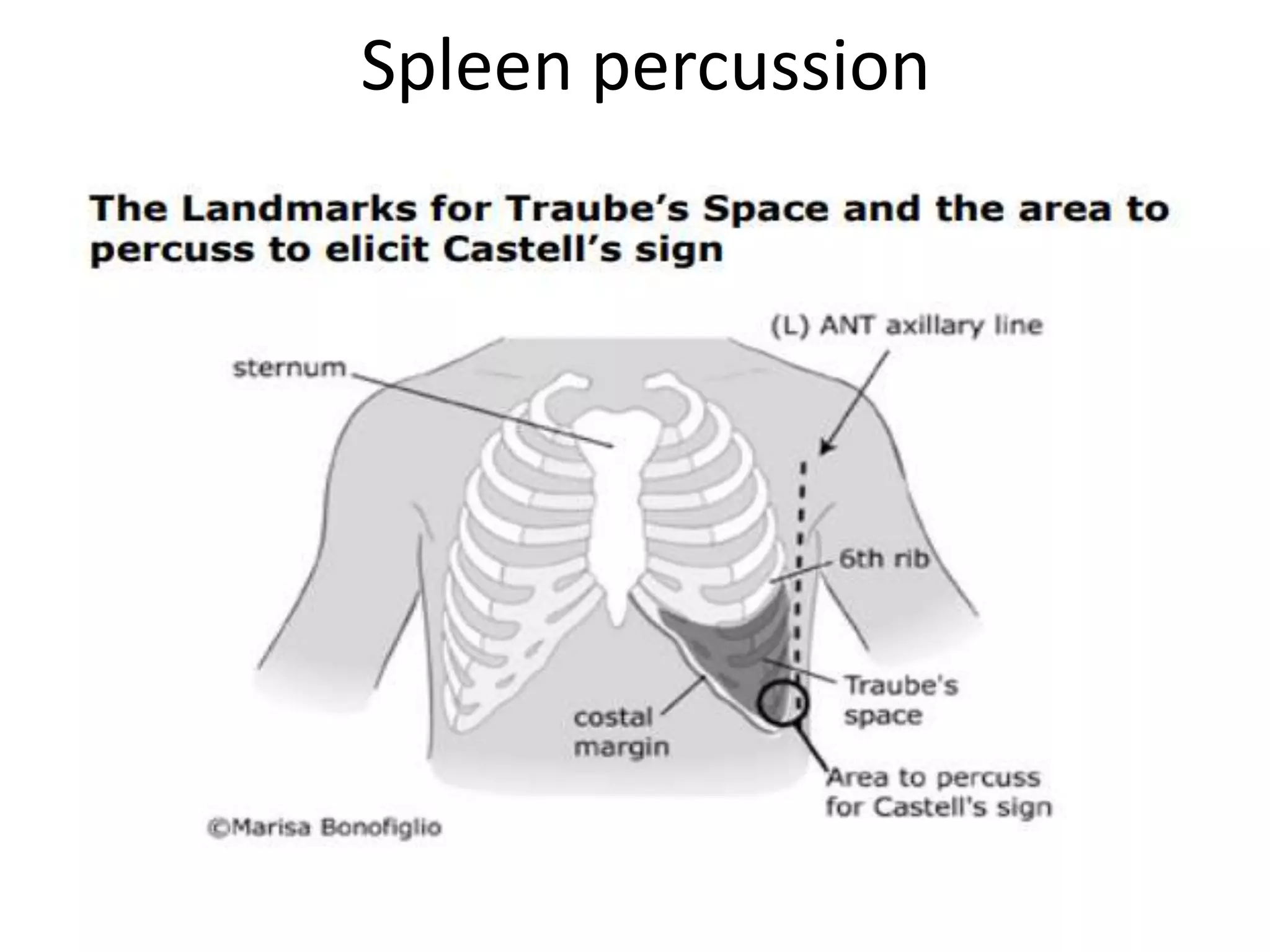
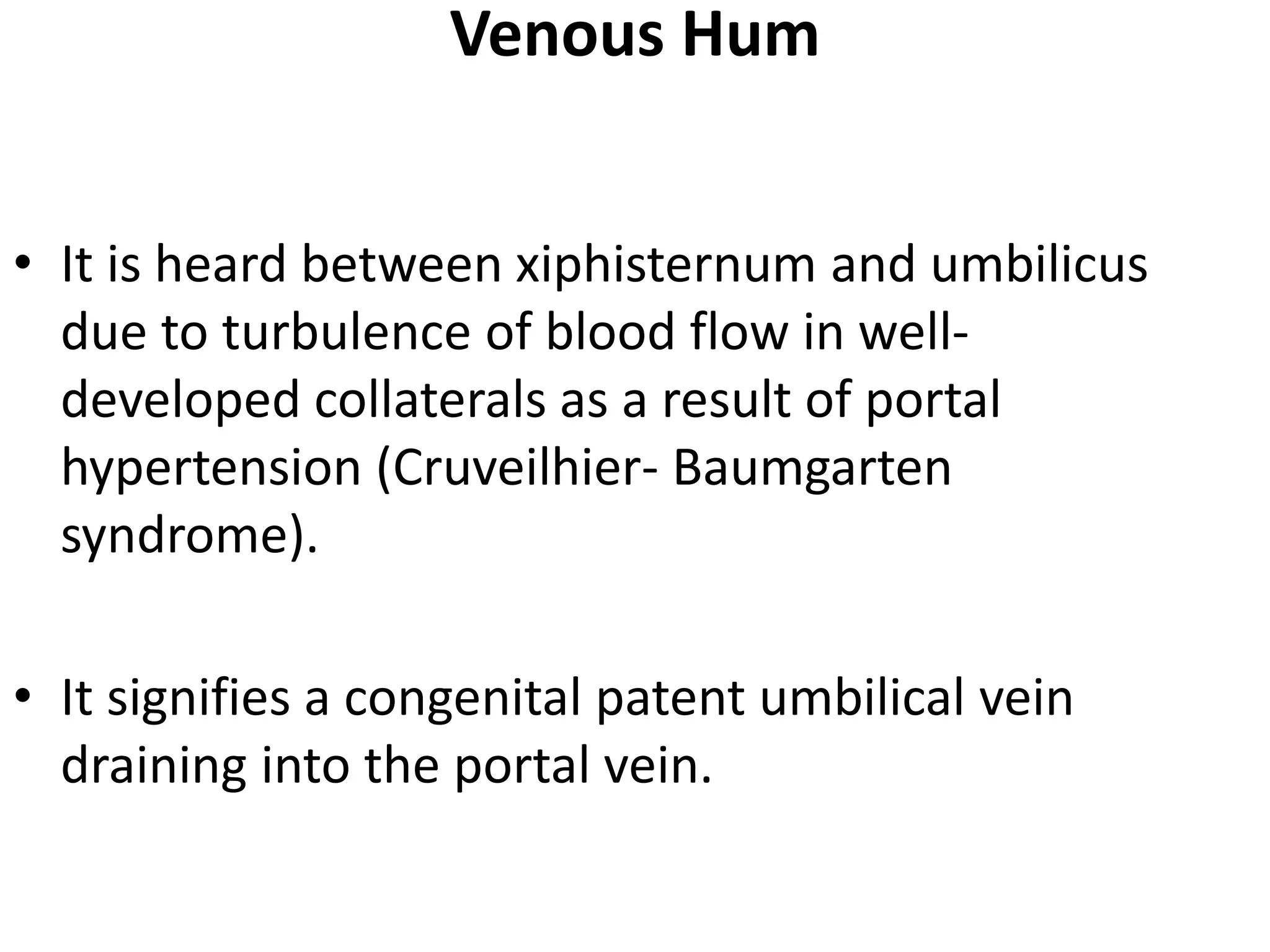
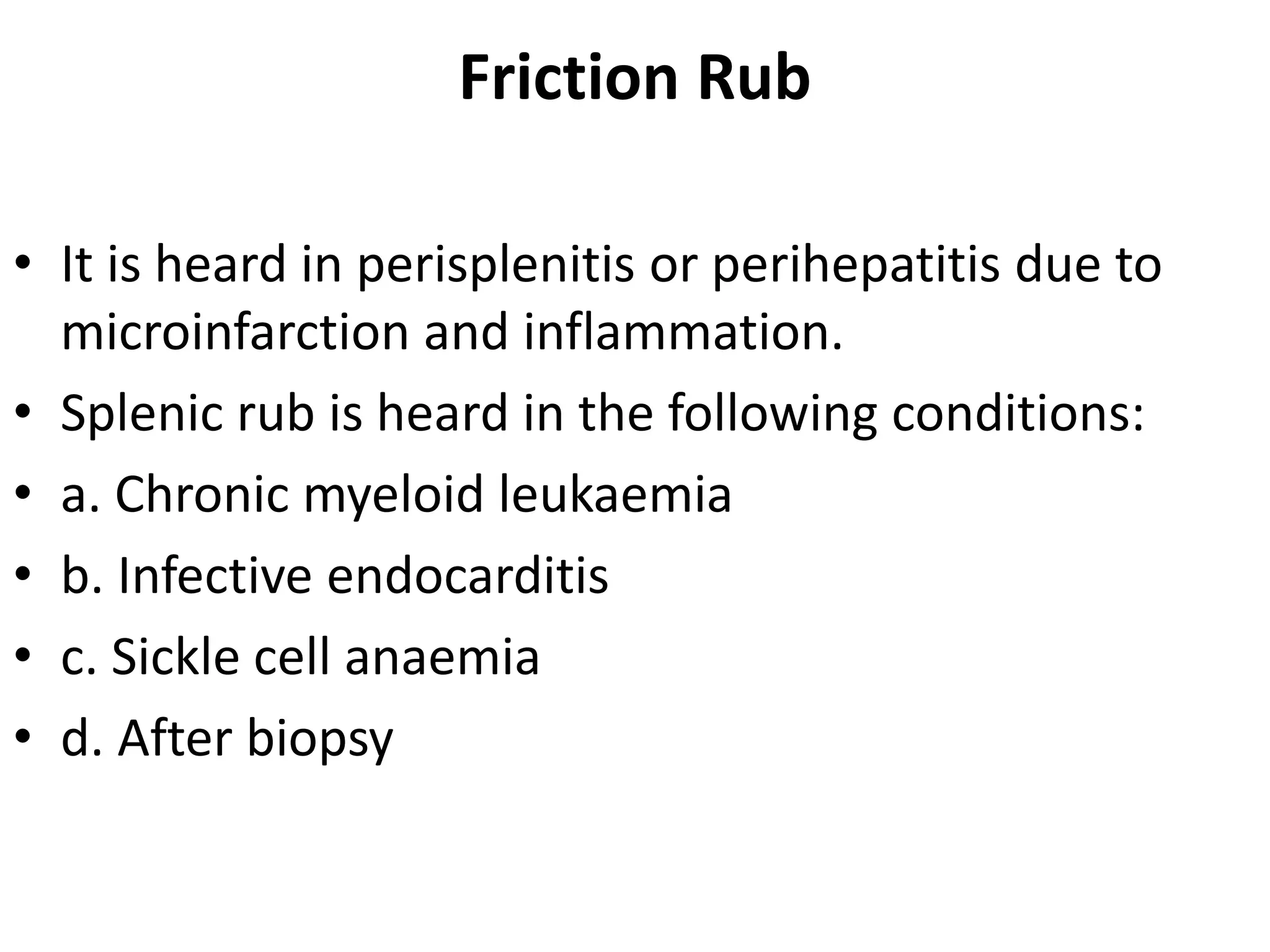
This document provides an overview of techniques for examining the abdomen through inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation. Key points covered include assessing the shape and movements of the abdomen, palpating the liver, gallbladder, spleen and kidneys, using percussion to define organ boundaries, and listening for bowel sounds, succussion splash, bruits, venous hum, and friction rubs over the abdomen. The document serves as a guide for medical students to perform a thorough physical examination of the abdomen.