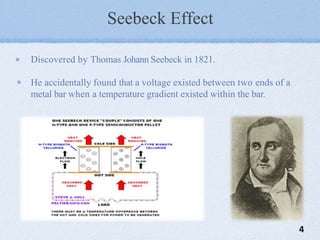
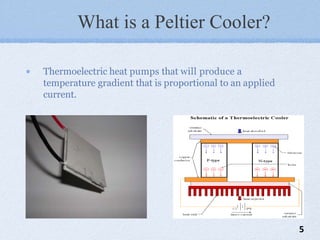
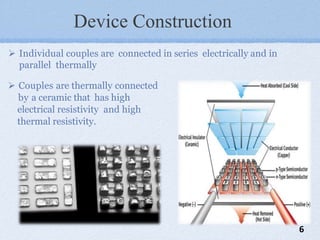
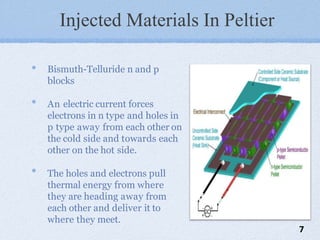
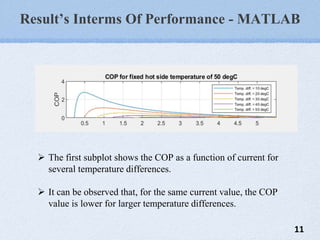
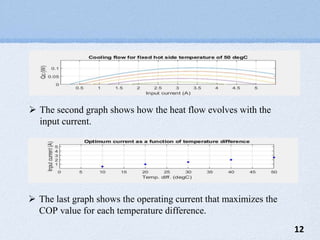
The document presents a mini project on the Peltier device as a thermoelectric cooler, detailing its principles, construction, and applications. It discusses the Peltier effect, which allows for temperature gradients through semiconductor technology, and reviews various studies and relevant literature on the subject. The document further analyzes the performance of Peltier modules using MATLAB simulations and outlines their pros and cons.