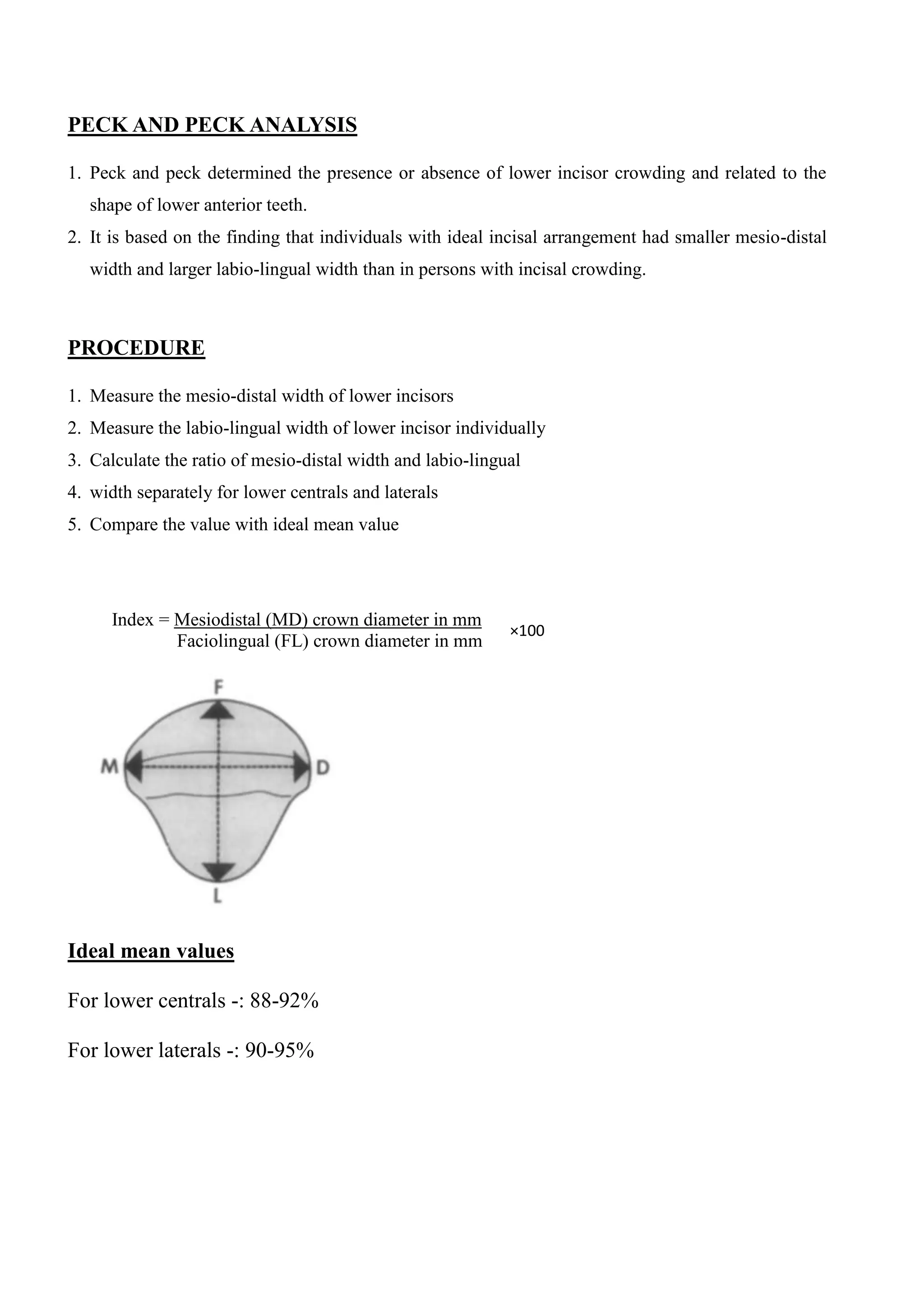
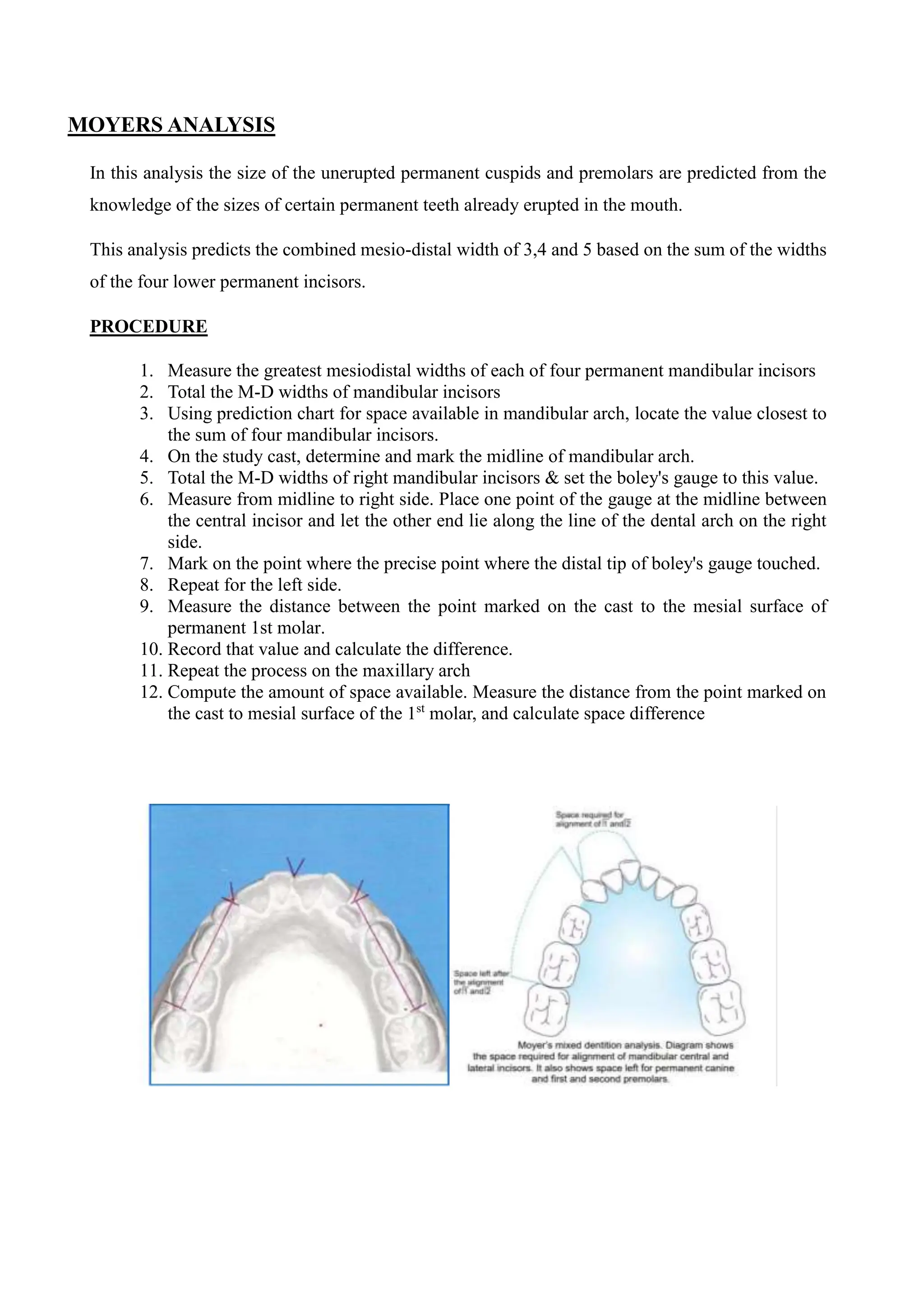
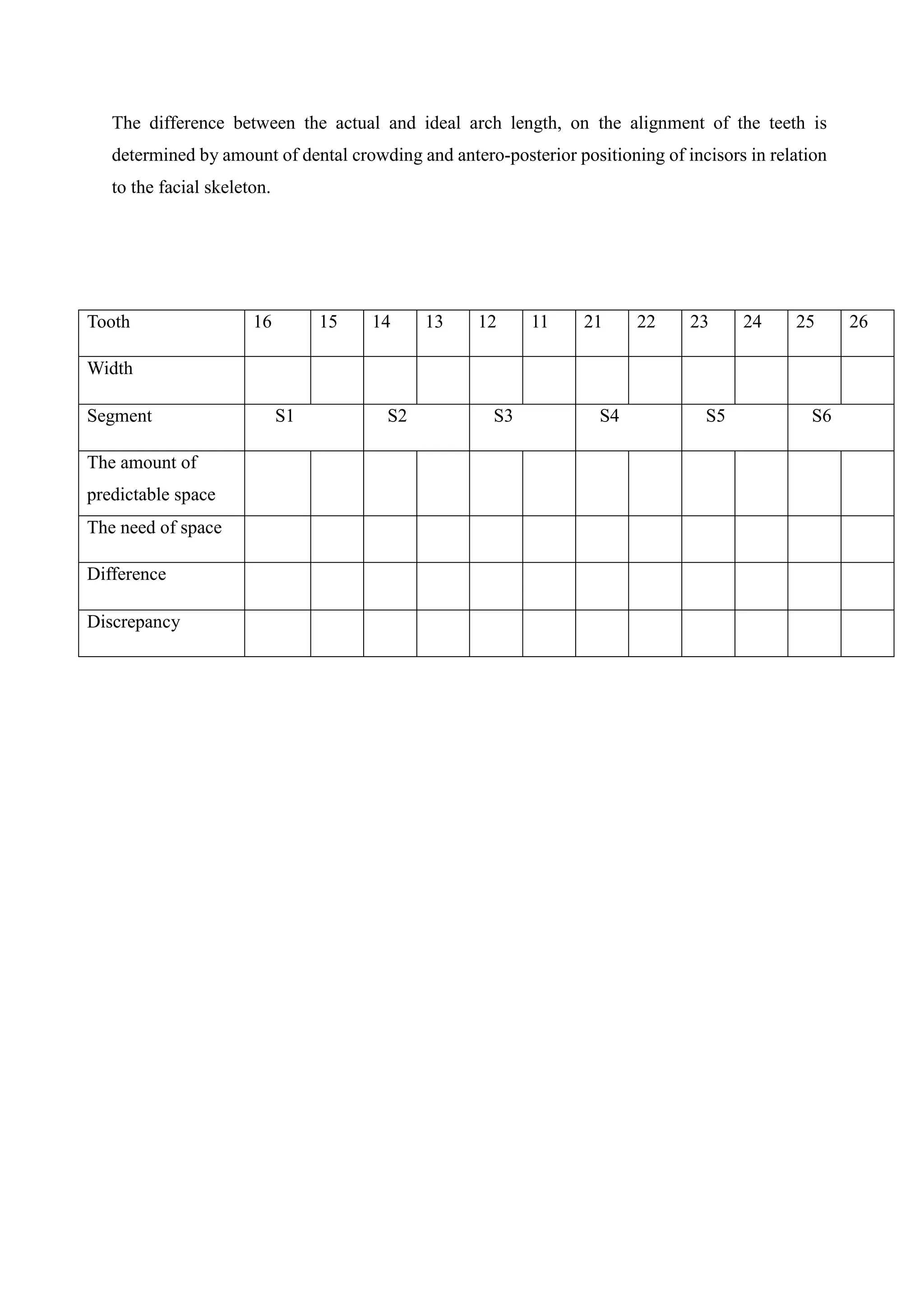
The document discusses various analyses used to assess dental arch measurements, focusing on lower incisor crowding and tooth dimensions. It outlines procedures for Peck and Peck analysis, Moyers analysis, and Lundstrom segmental analysis, detailing measurement techniques and calculations for determining tooth width and available space. Ultimately, these analyses aid in understanding dental crowding and the positioning of teeth in relation to the ideal arch length.