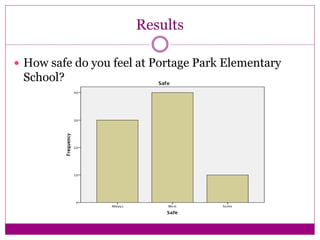
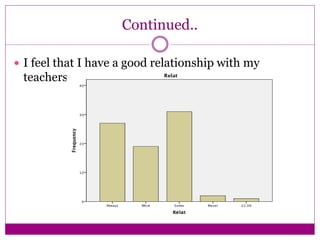
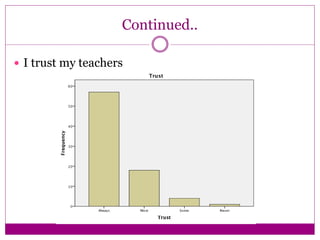
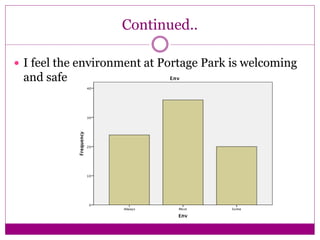
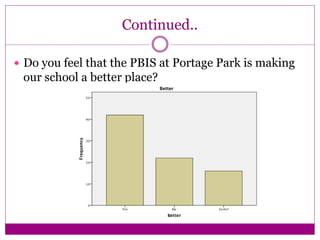
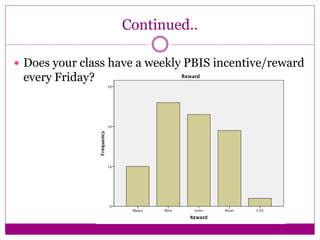
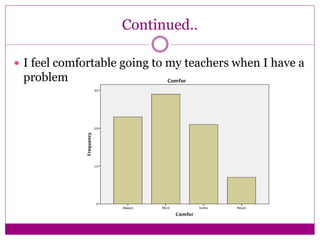
The document discusses the implementation and assessment of Positive Behavior Intervention Supports (PBIS) at Portage Park Elementary School. PBIS is designed to promote positive behavior and eliminate challenging behaviors. The school implements PBIS through a goals matrix, rewarding good behavior with tickets, using the Second Step curriculum, and providing point sheets for students who need extra support. To assess PBIS effectiveness, the author surveyed 80 students in grades 2-5 about how safe and welcoming they feel at school and if PBIS is improving the environment. Preliminary results found students feel safe and have good relationships with teachers, but more specific PBIS-focused questions should be asked. The author concludes there has been positive change since PBIS but room for improvement