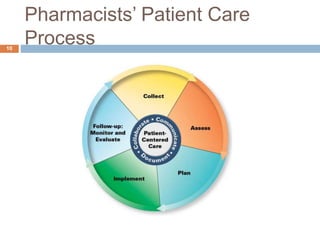
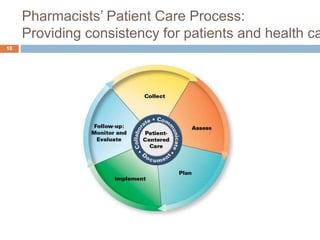
This document describes the development of the Pharmacists' Patient Care Process by the Joint Commission of Pharmacy Practitioners. The process was created to standardize how pharmacists deliver patient-centered care across different practice settings. It consists of five elements: collect, assess, plan, implement, and follow-up/monitor & evaluate. Various pharmacy organizations have endorsed the process, which is being promoted through education, quality measures, and implementation projects. The goal is for the process to facilitate consistency and quality in pharmacists' patient care services.