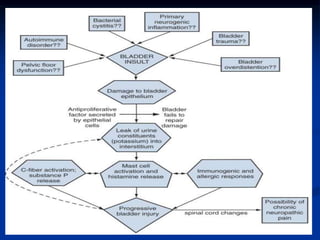
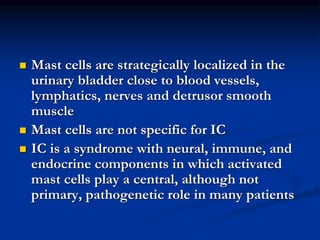
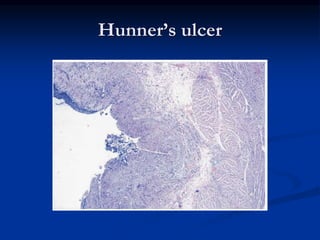
This document summarizes the pathogenesis of interstitial cystitis (IC). It discusses how IC was originally described in the 1800s and defines how it is currently classified. The pathogenesis is multifactorial and may involve infection, inflammation, autoimmunity, mast cell involvement, defects in the bladder surface, and neurobiological factors. The document also reviews diagnostic criteria, epidemiology, associated disorders, potential etiologies, and pathological findings of IC.