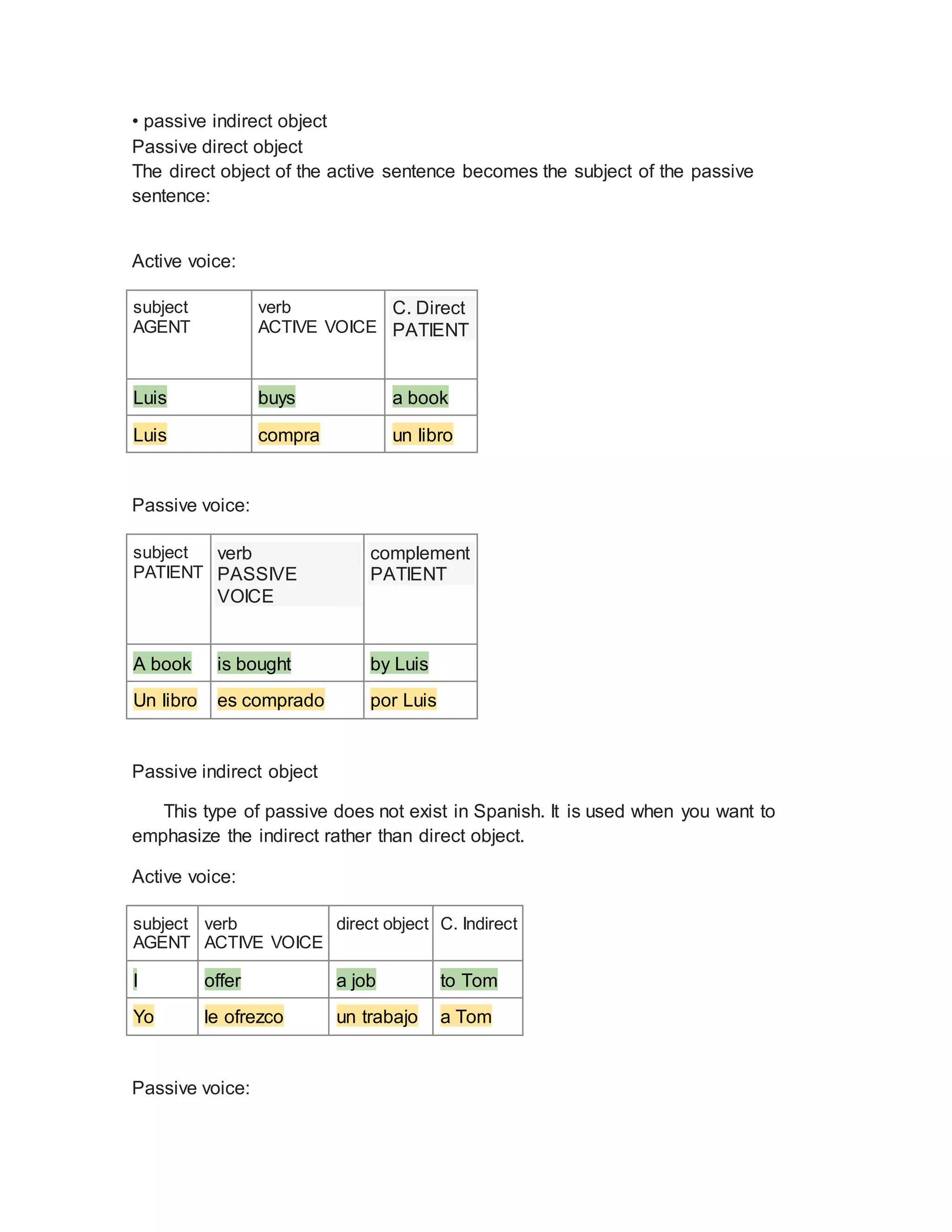
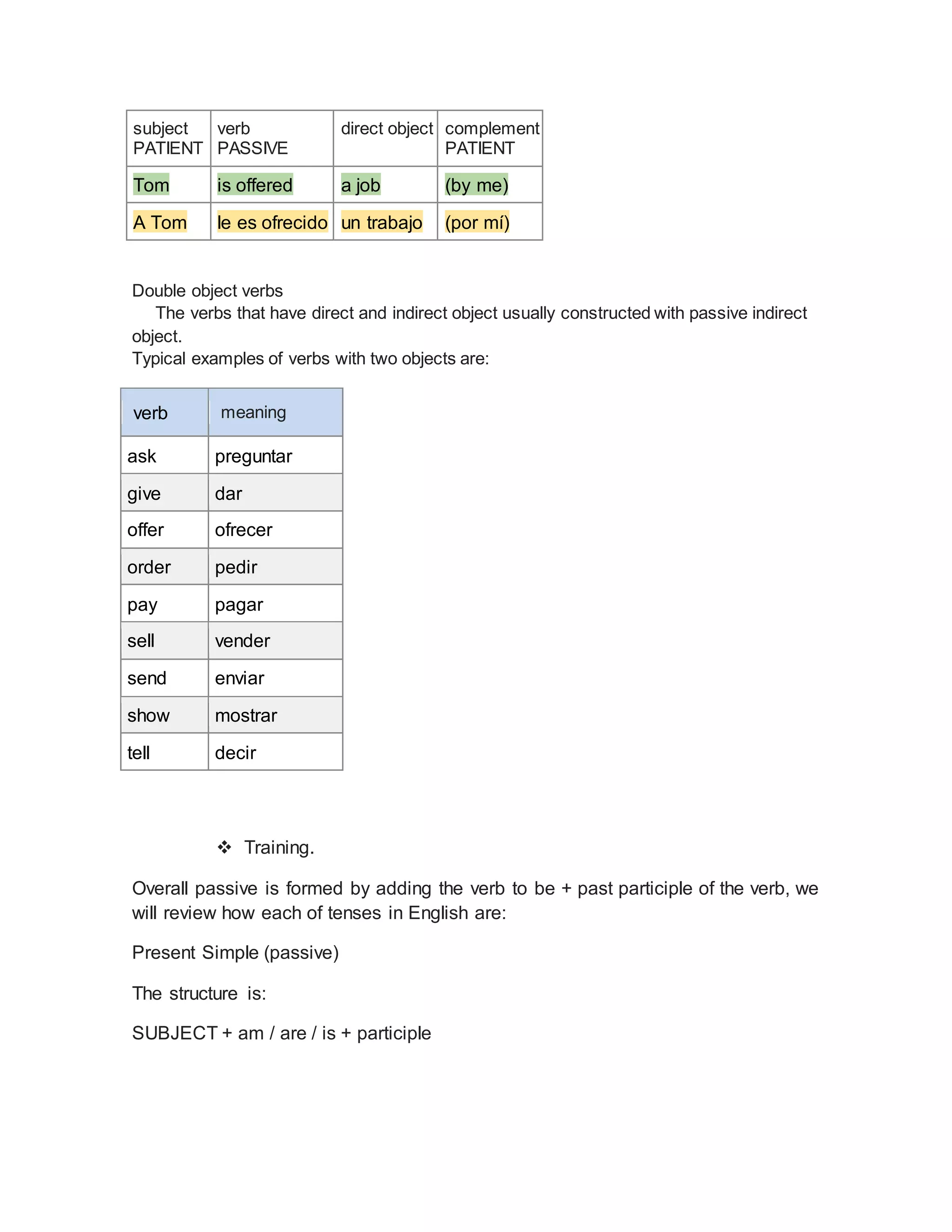
This document defines and explains the passive voice in English grammar. It begins by defining the passive voice as a grammatical construction where the subject of the sentence expresses the theme or patient of the verb's action rather than the agent. It then provides examples of active and passive sentences. The rest of the document outlines the different forms of the passive voice based on English verb tenses. It explains how to form the passive voice for simple present, present continuous, present perfect, and other tenses. It also discusses how to use the passive voice with modal verbs.