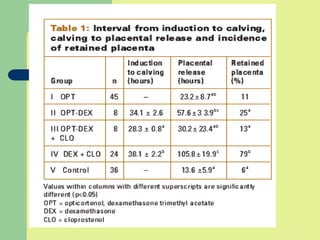
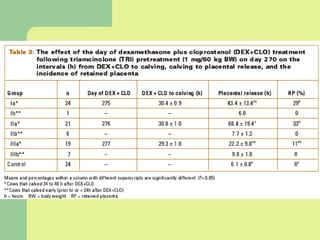
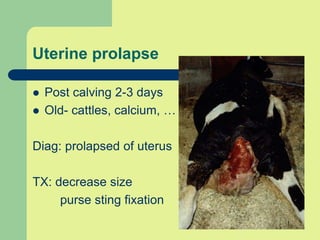
This document discusses parturition and induction of parturition in various livestock species. It provides information on the average gestation lengths for cattle, goats, sheep, and swine. It then describes the three stages of parturition and the hormonal changes that occur leading up to birth. The signs of approaching parturition are also outlined for cattle, sheep, and goats. The document concludes by discussing various methods for inducing parturition in cows, ewes, and goats, as well as some potential post-calving problems.