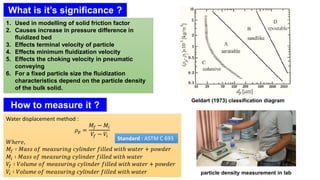
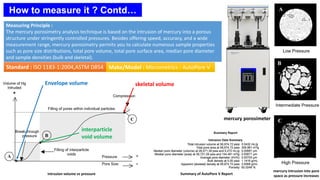
Particle density is defined as the ratio of the mass of a particle to its volume, varying for non-porous and porous particles. Measurement methods include water displacement and pycnometry techniques that assess the volume of a sample and its interaction with fluids. Significance includes its effects on fluid dynamics, such as fluidization characteristics and terminal velocities.