The document discusses different aspects of business models including:
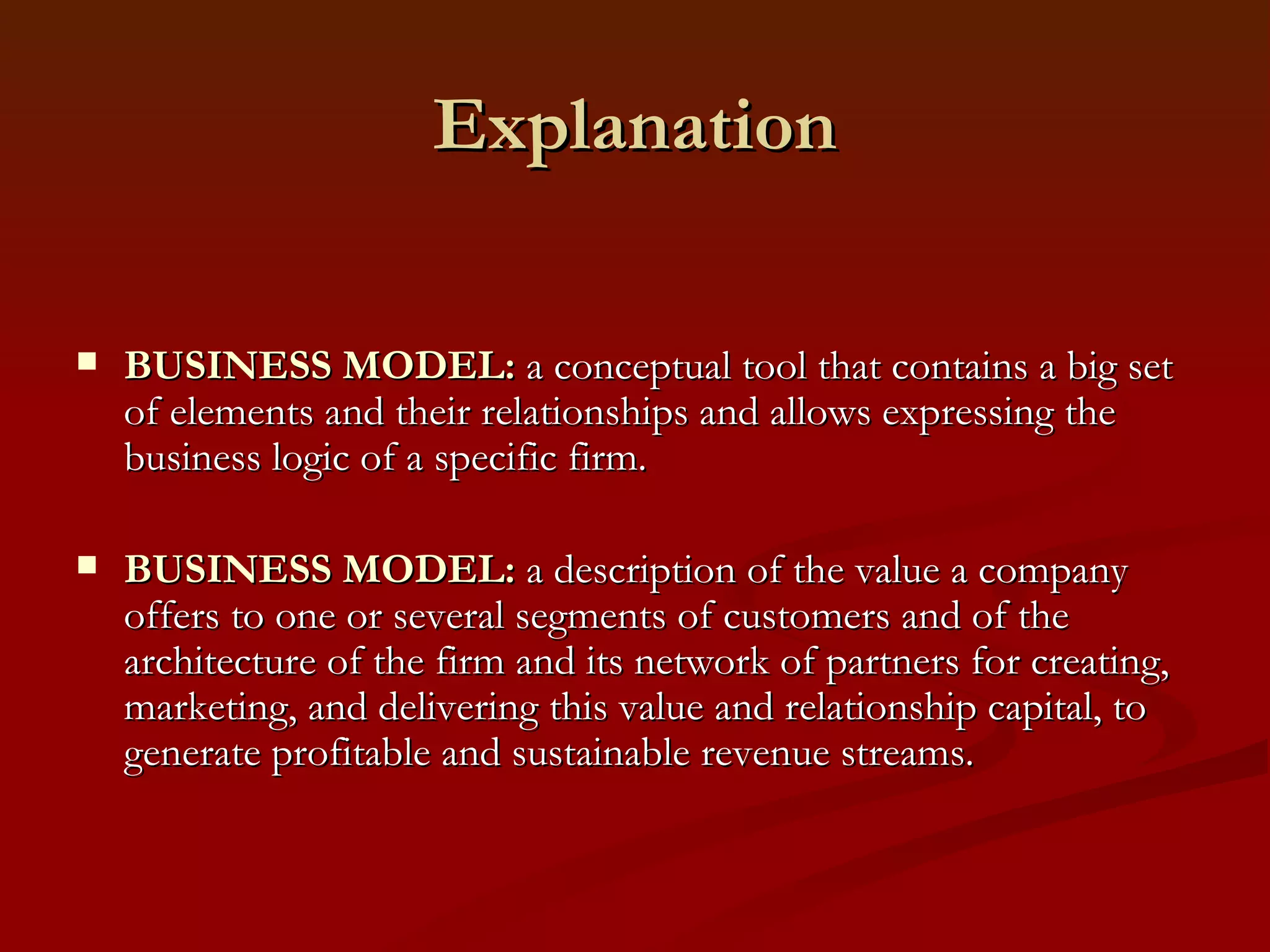
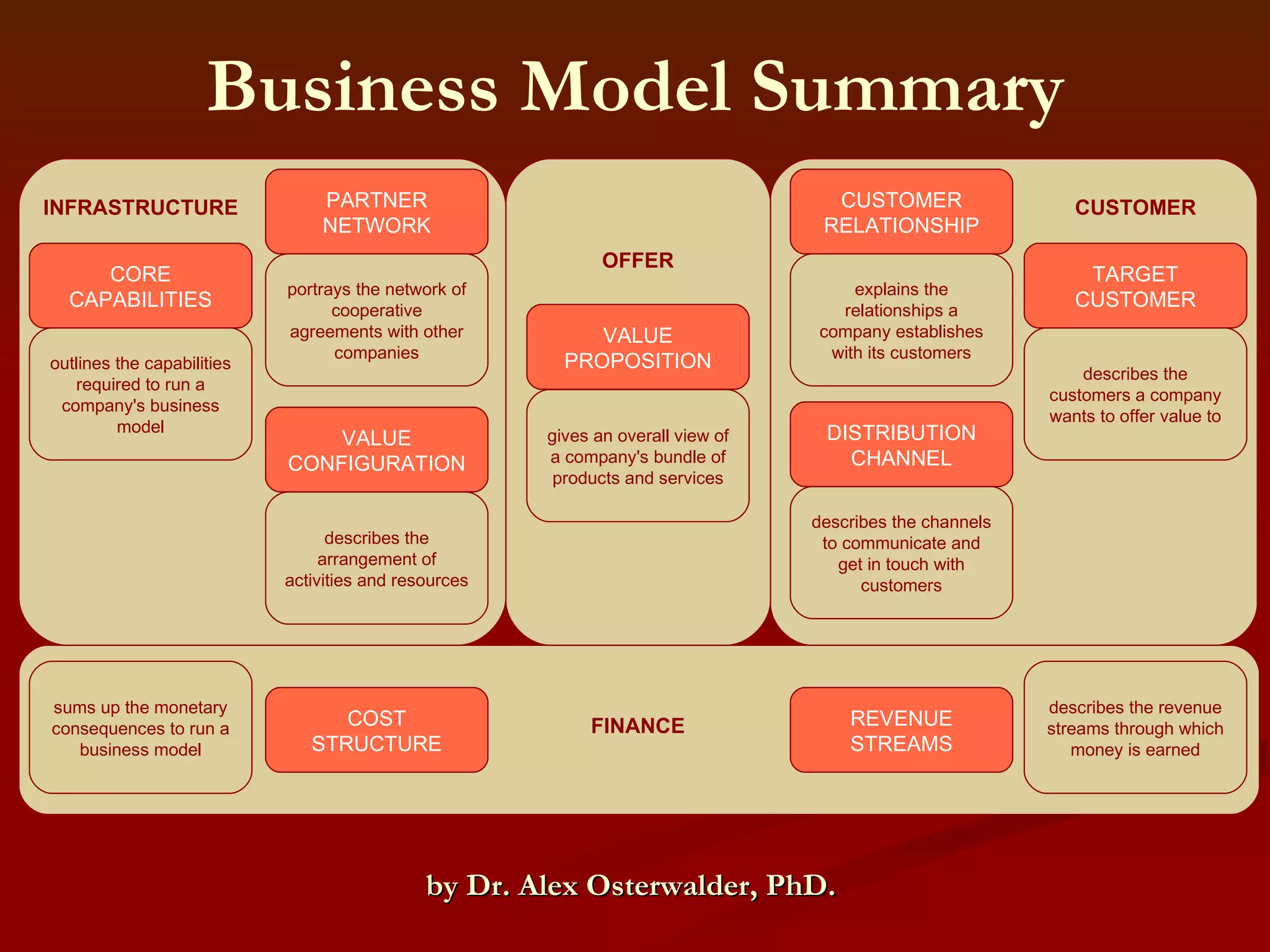
1. It defines a business model as a conceptual tool that represents various elements of a business such as offerings, strategies, infrastructure, and processes.
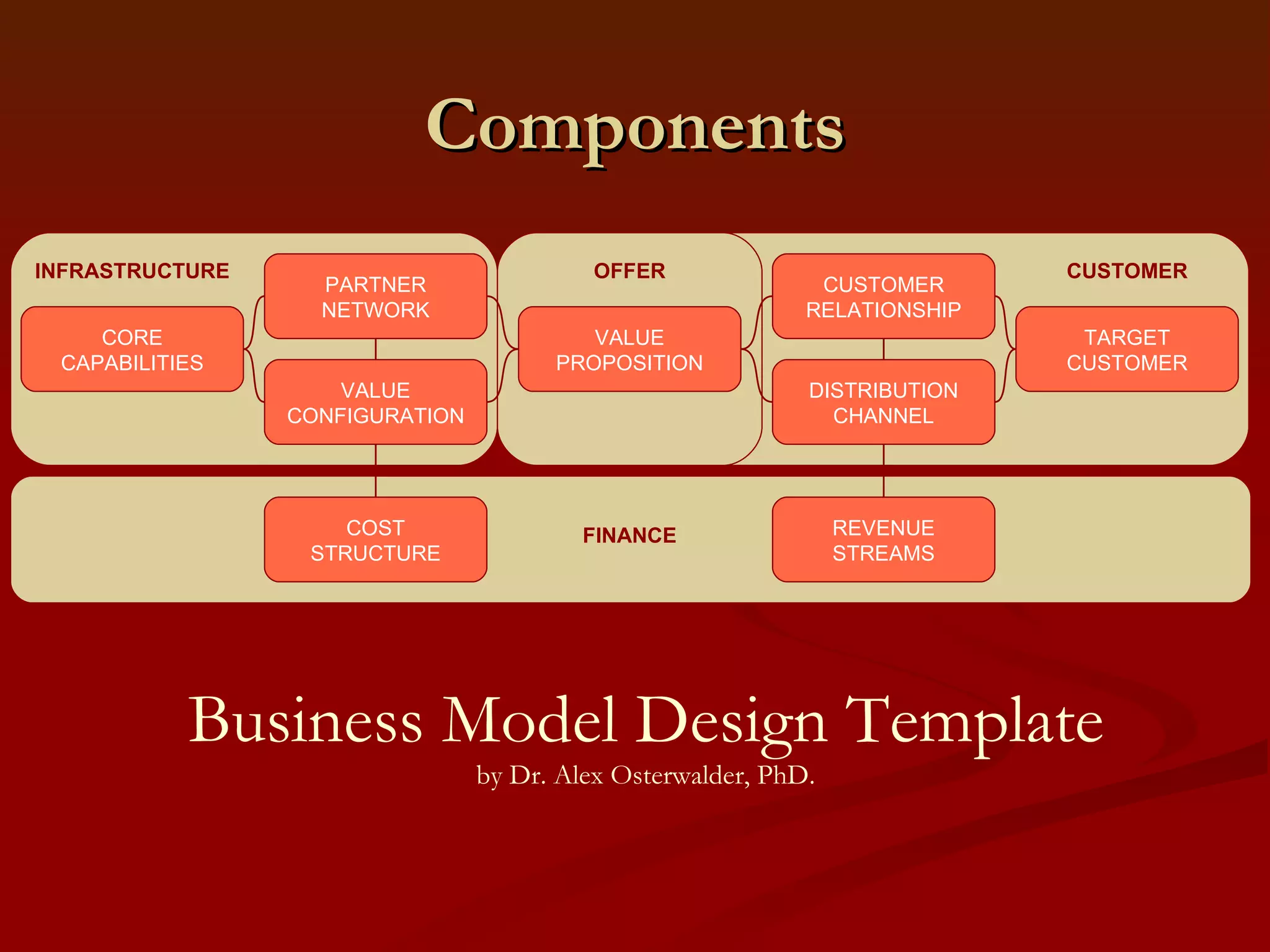
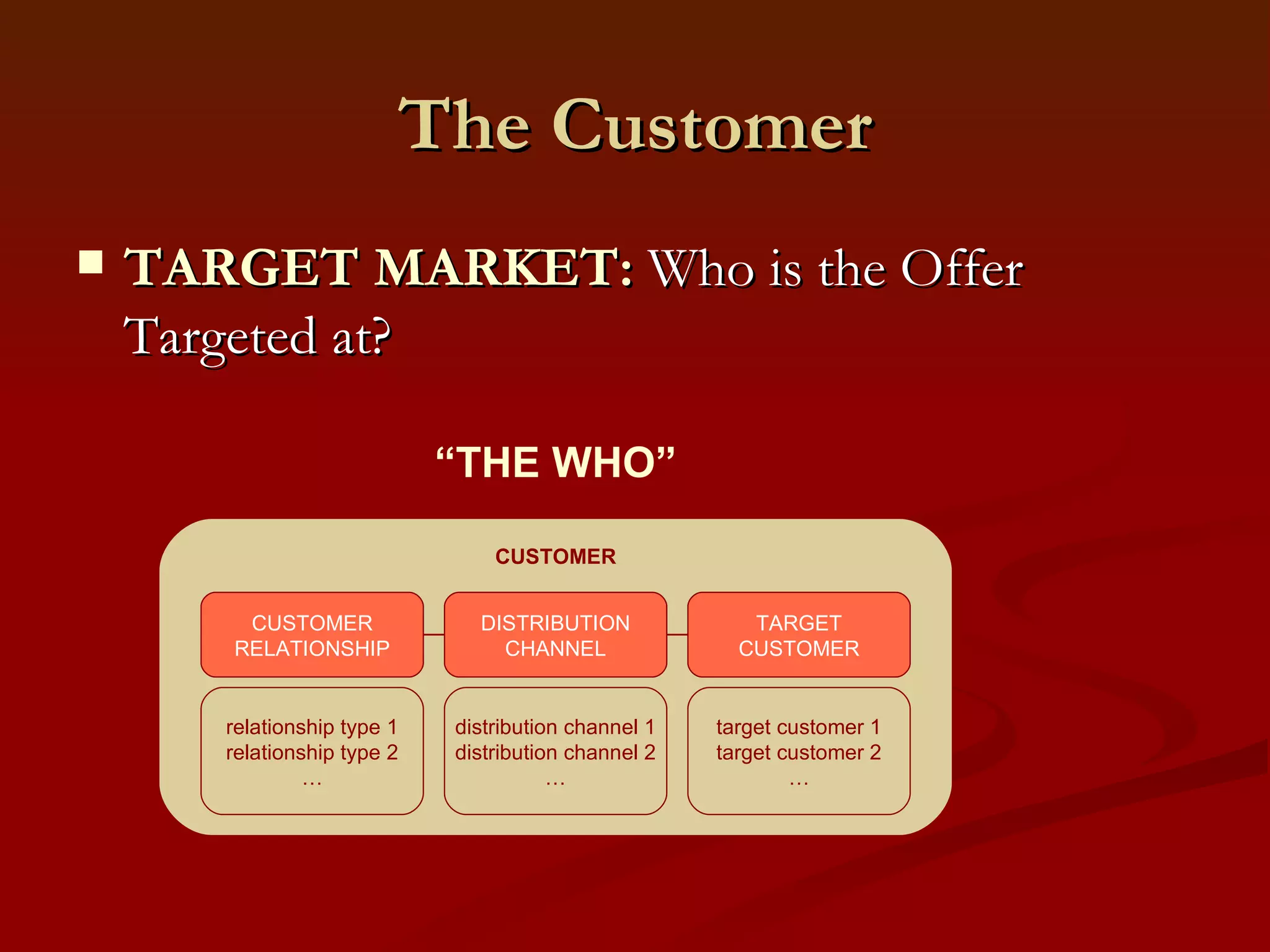
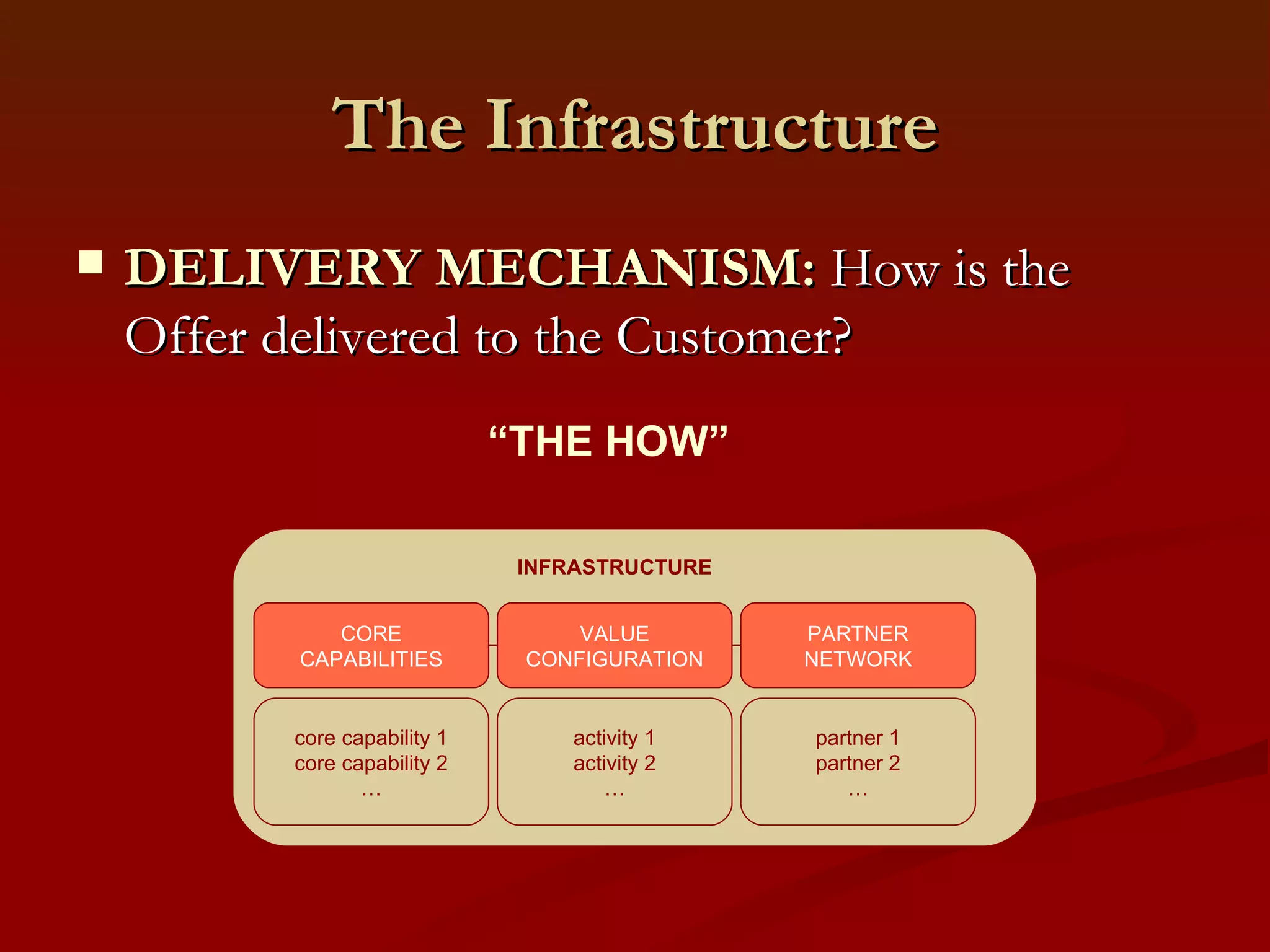
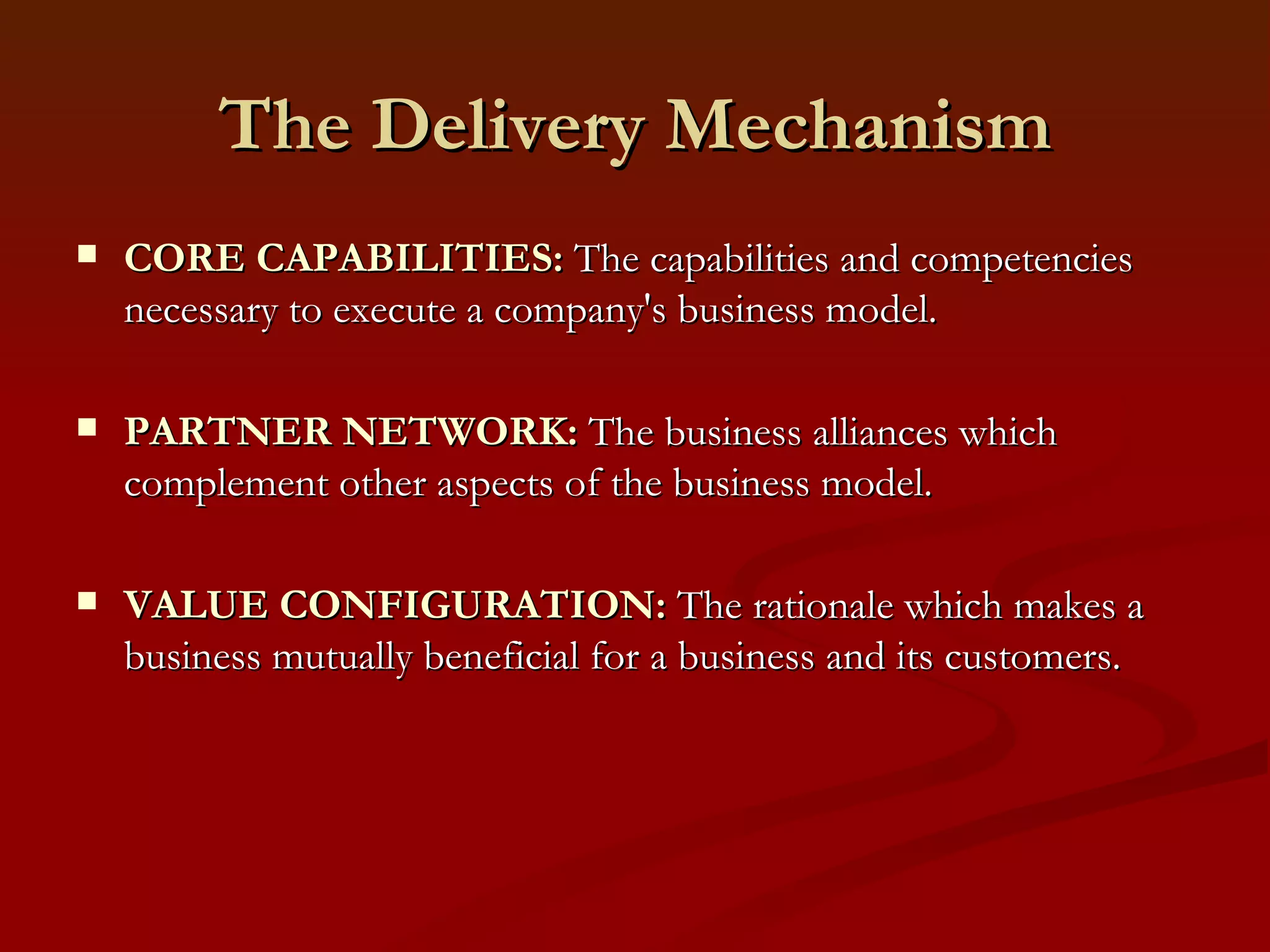
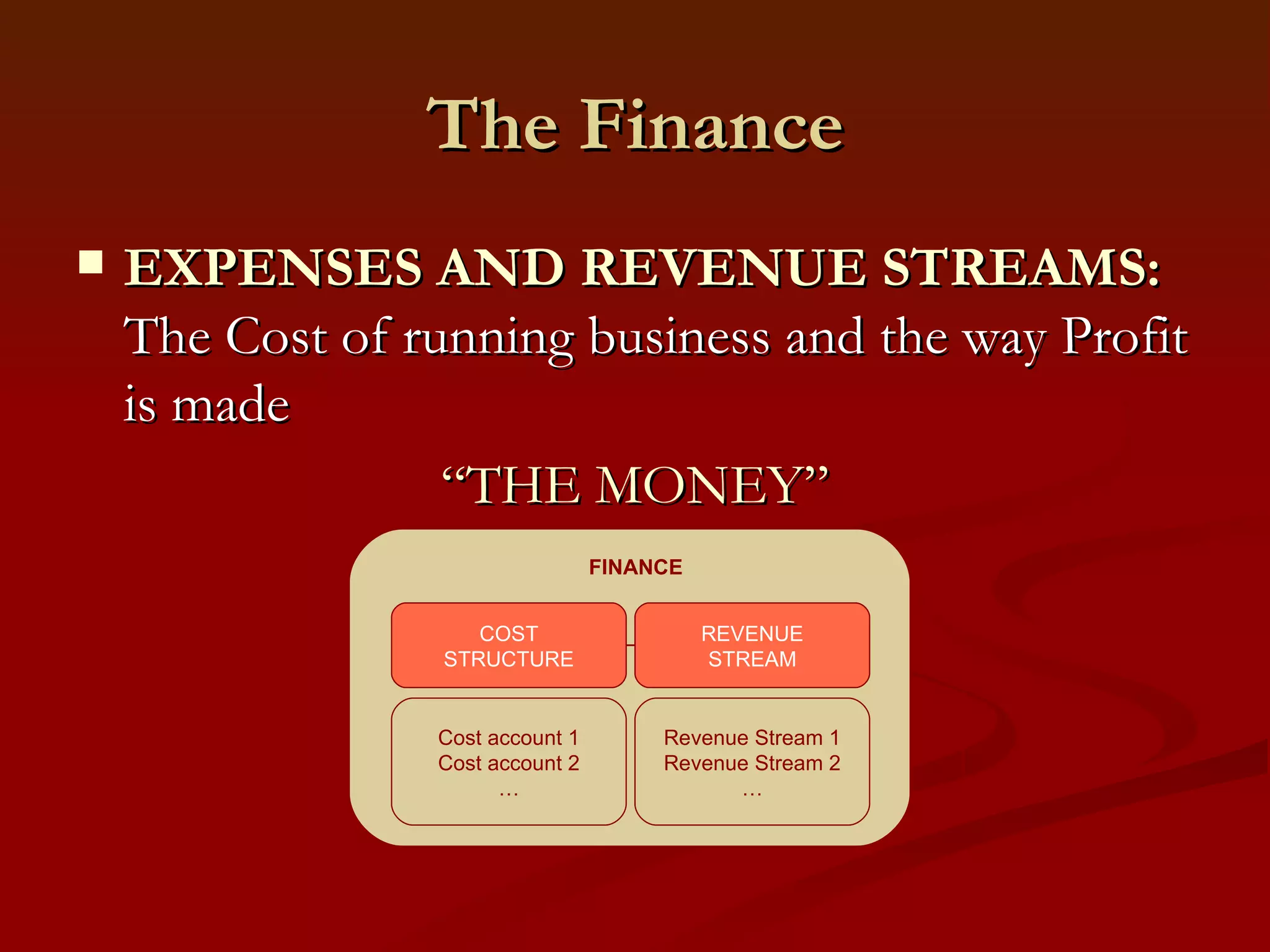
2. It outlines the key components of a business model including value proposition, customer relationships, revenue streams, resources, and processes.
3. It explains that a business model should create value for customers and capture value for the business through competitive advantages.