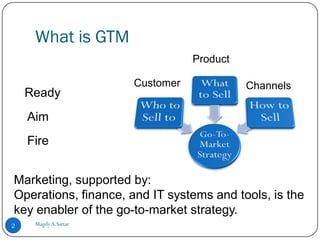
This document outlines the key steps to developing an effective go-to-market strategy. It discusses defining the market opportunity, building a budget model with clear goals, identifying the overall strategy for delivering the product or service, outlining specific tactics for the first year, and identifying and managing risks. Key elements include understanding market dynamics, setting revenue and margin targets, determining how the service will be delivered and why customers will buy it, defining required organizational changes and marketing activities, and establishing metrics to monitor strategy success over time.