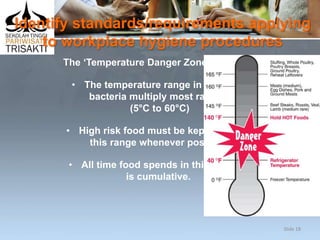
This document outlines procedures for complying with workplace hygiene in food handling. It discusses identifying relevant hygiene procedures, standards, and risks. Key points include following legislation and enterprise policies on food receiving, storage, preparation, service and cleaning. Personal hygiene for food handlers like handwashing, protective clothing, and covering cuts is emphasized. Identifying and reporting any unsafe food handling practices is also covered.