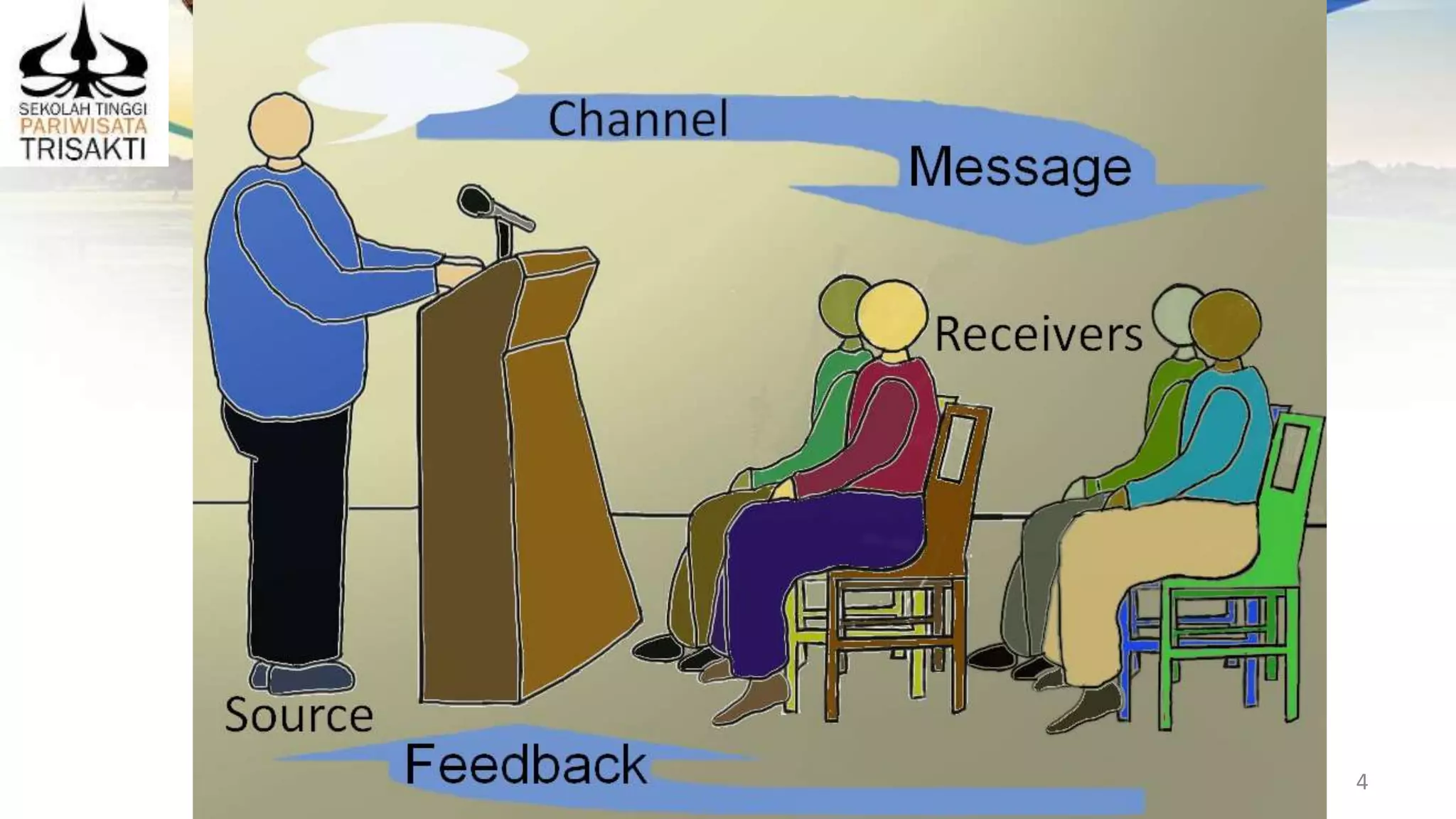
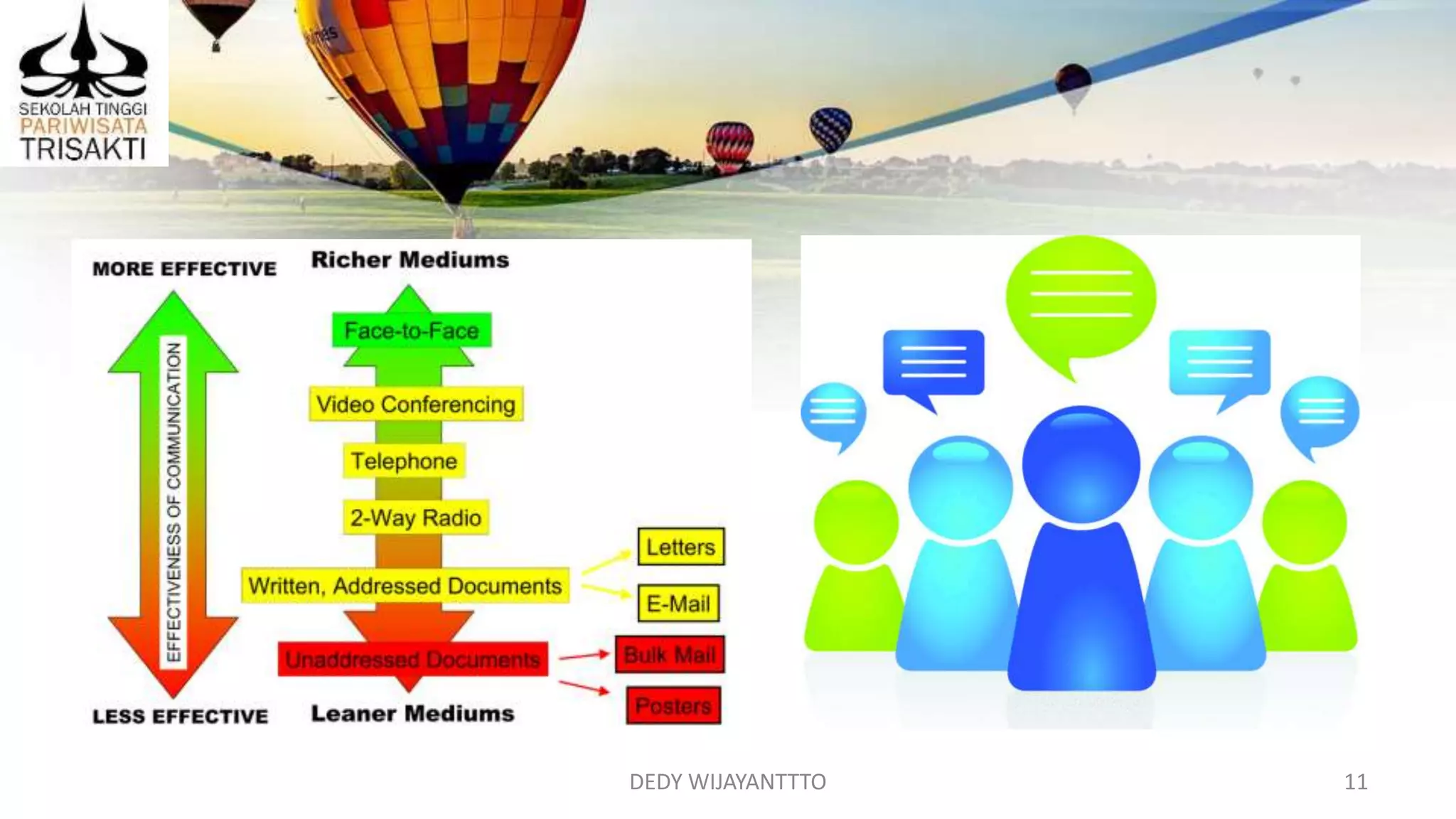
The document discusses various approaches to developing and supervising staff as a manager. It covers providing feedback to employees, monitoring performance, identifying training opportunities, and being an effective leader and role model. Specific topics include giving positive and negative feedback, using checklists to monitor work, providing formal and informal learning programs, mentoring and coaching employees, and qualities of successful managers such as competence, leadership abilities, and managing oneself well.