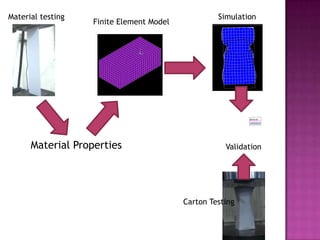
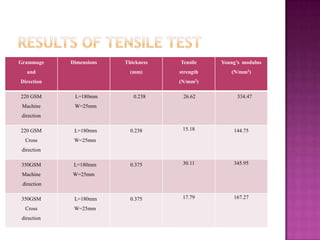
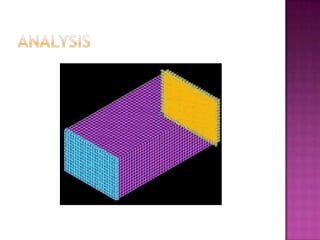
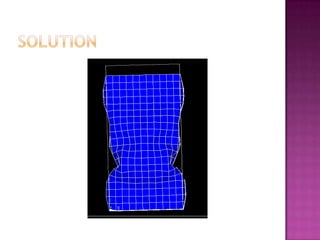
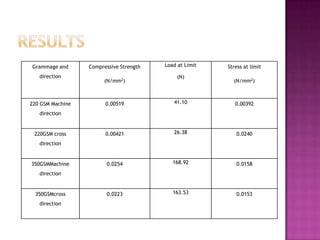
The document discusses creating an accurate finite element model of paper cartons to replace physical testing. It involves creating the finite element model, conducting physical testing for validation, simulating loads, and validating results. Material properties are tested and used to refine the finite element model. Simulation results are compared to physical testing which show good agreement within 10% for force and 4mm for peak displacement. The finite element model is found to be reliable with potential for improving the modeling of creasing phenomena.