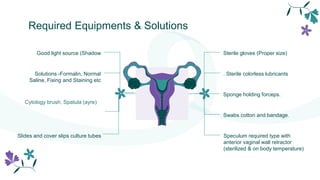
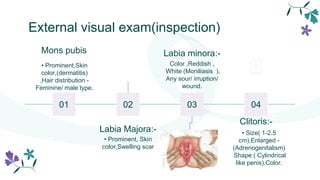
This document provides information about pelvic examinations and pap smears. It defines a pelvic exam as a physical examination of the external and internal female pelvic organs used to evaluate symptoms affecting the female reproductive and urinary tract. It describes the various components of a pelvic exam including external visual inspection, speculum exam, bimanual exam, and pap smear. It outlines the necessary equipment, procedures, potential complications and recommendations for pap smear screening. The conclusion summarizes that regular pelvic exams and pap smears are important for early detection and prevention of cervical cancer.