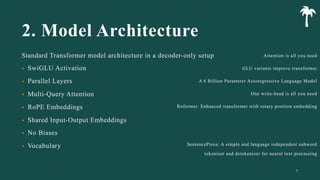
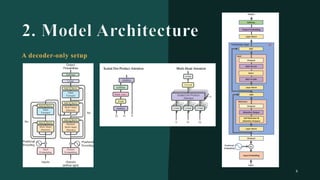
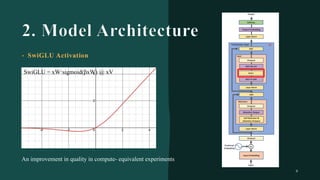
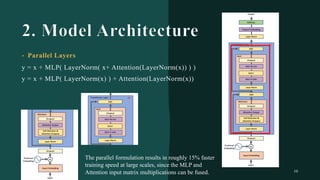
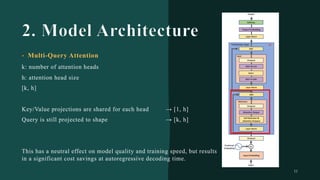
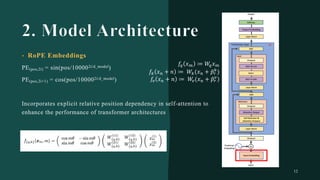
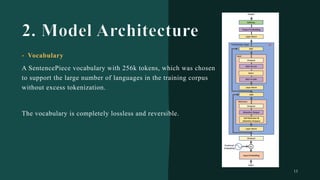
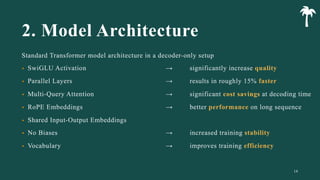
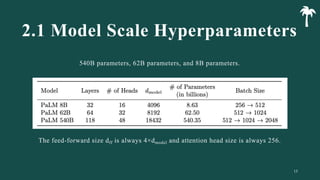
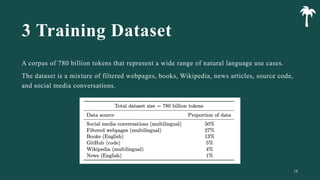
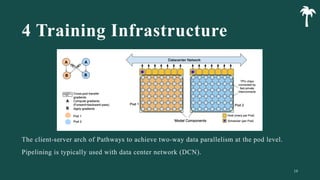
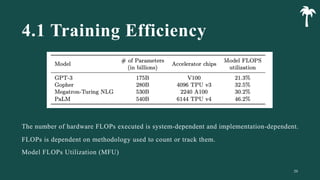
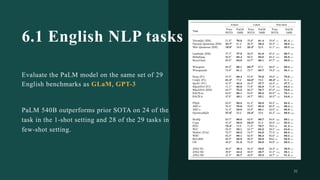
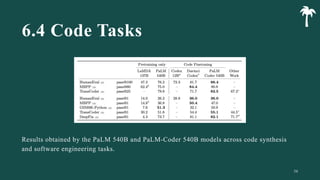
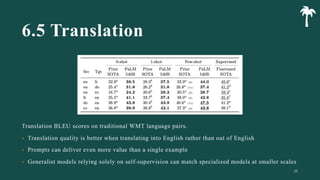
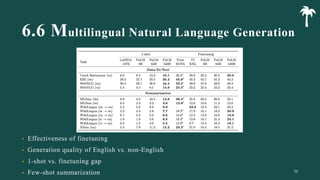
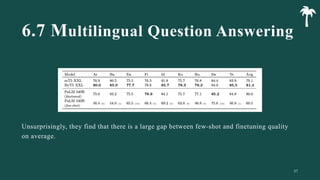
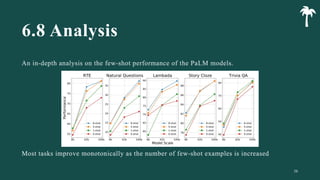
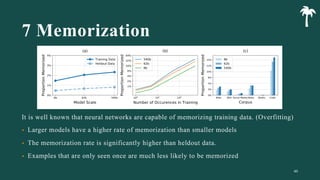
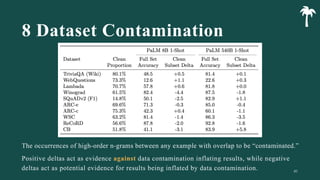
대규모 언어 모델은 적은 양의 학습 데이터로도 탁월한 성능을 발휘하여 다양한 자연어 처리 작업에서 매우 유용하게 사용됩니다. 이에 대한 이해를 더하기 위해, 구글은 PaLM이라는 5400억 개의 매개변수를 가진 언어 모델을 새로 개발하여, 다양한 자연어 이해 및 생성 작업에서 최첨단의 성능을 보여주고 있습니다. 이 모델은 Pathways라는 새로운 ML 시스템을 이용하여 6144개의 TPU v4 칩을 사용하여 학습되었습니다. PaLM은 다양한 과제에서 뛰어난 성능을 보이며, 특히 멀티스텝 추론 작업에서 최고의 성능을 발휘하여 인간 수준 이상의 결과를 달성하였습니다. 또한 다국어 작업과 소스 코드 생성 작업에서도 강력한 성능을 보이며, 편향성 및 독성에 대한 종합적인 분석과 모델 규모에 따른 학습 데이터 기억력 연구에 대한 결과도 제공합니다. 마지막으로, 대규모 언어 모델에 대한 윤리적 고민과 이를 완화하기 위한 전략에 대해 논의합니다.