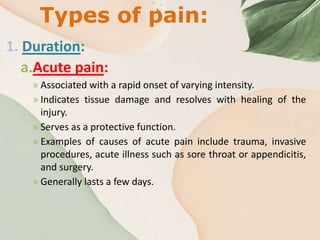
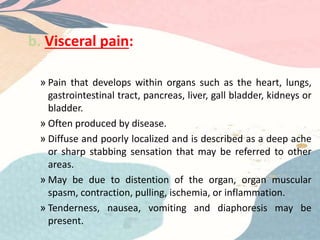
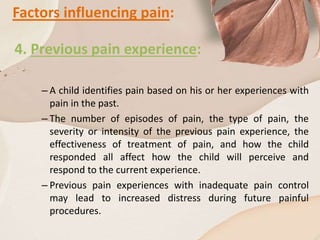
Pain is a complex, subjective experience that can affect people of any age. It is defined as an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. Pain can be acute or chronic and results from various causes including disease, injury, and medical procedures. It is influenced by factors like age, gender, cognitive ability, temperament, previous pain experiences, family/culture, and current situational factors. Proper pain management is important for comfort and has benefits like reduced anxiety and need for restraints during medical procedures.