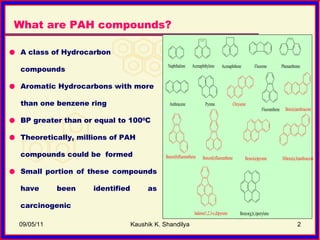
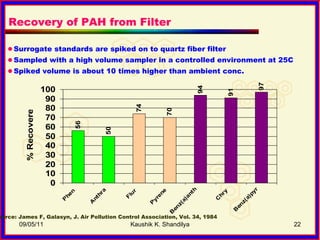
The document discusses polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), which are formed during incomplete combustion and contain multiple benzene rings. PAHs are emitted from sources like coal combustion, vehicle exhaust, and biomass burning. They can exist in both vapor and particle phases depending on their vapor pressure. Common techniques for sampling PAHs include collecting particles on filters and vapors on adsorbents like polyurethane foam. Proper sampling and storage methods are needed to minimize PAH degradation prior to analysis.