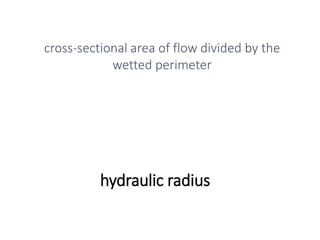
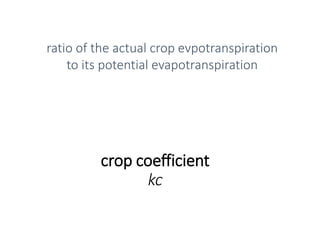
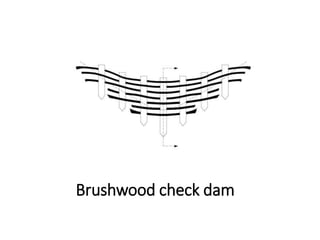
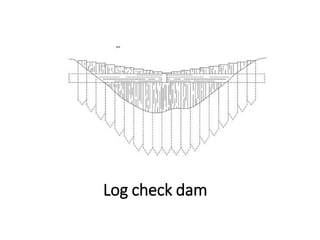
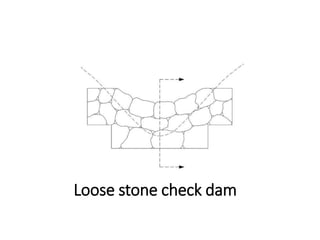
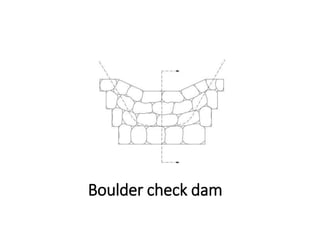
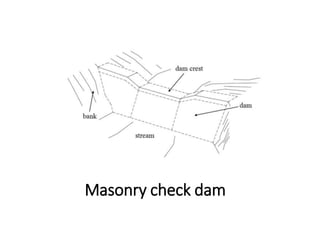
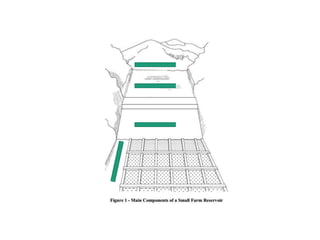
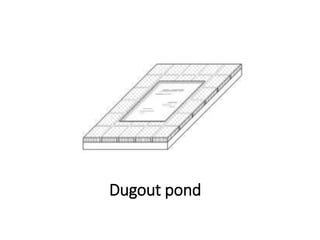
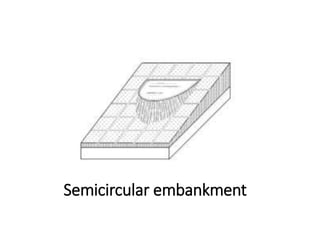
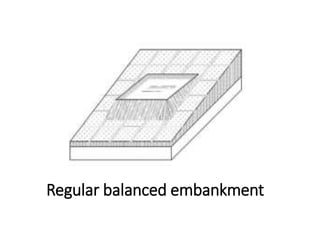
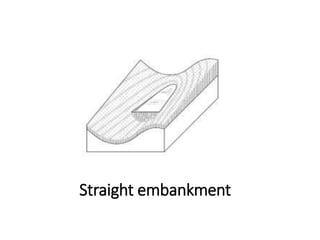
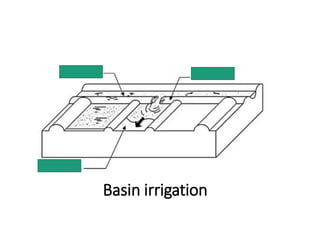
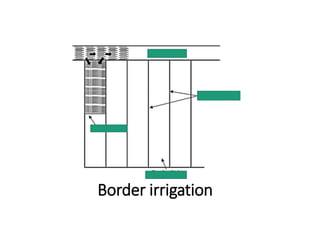
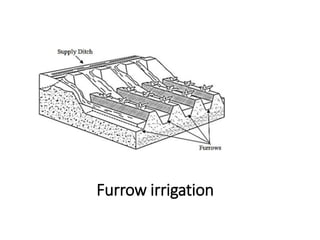
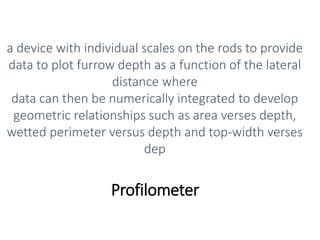
The document provides a comprehensive overview of various terms and concepts related to irrigation, including definitions of different irrigation methods, water management practices, and hydrologic principles. It addresses parameters such as crop evapotranspiration, conveyance efficiency, and effective rainfall, while also discussing structures like dams and channels. The document serves as a technical reference for agricultural engineers and water resource managers involved in irrigation projects.