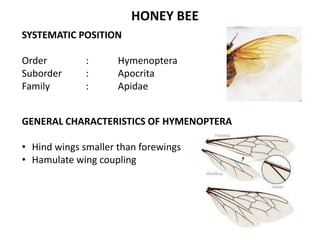
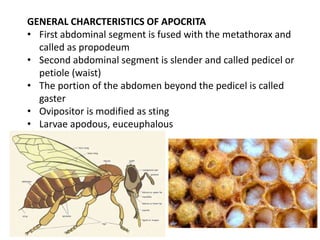
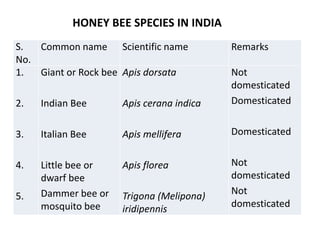
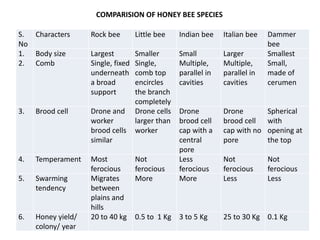
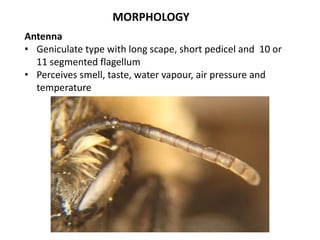
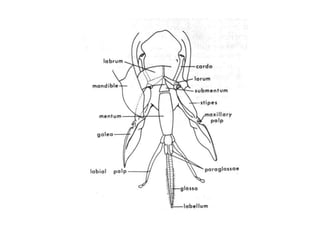
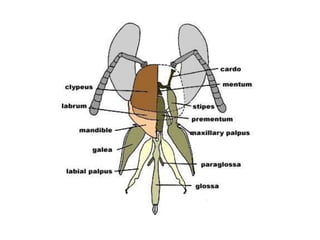
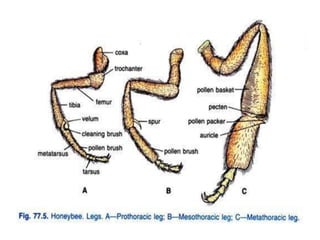
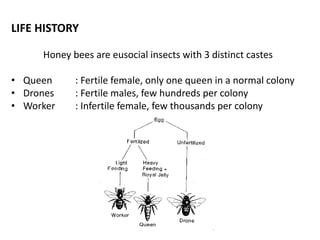
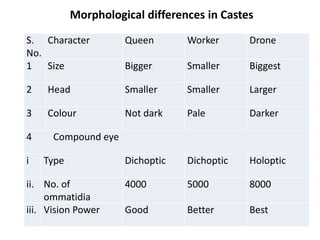
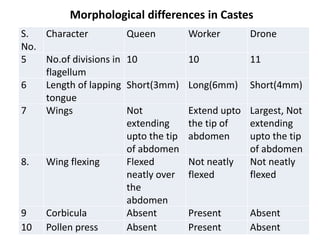
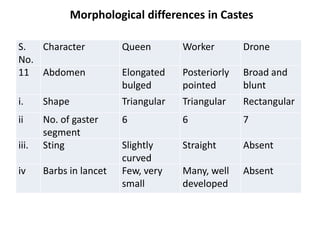
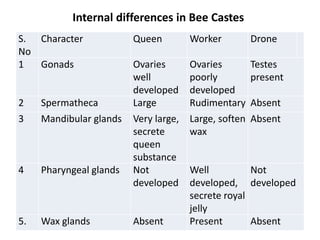
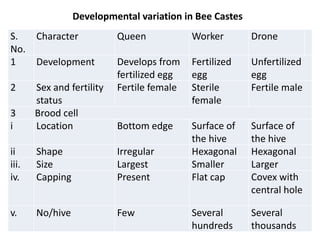
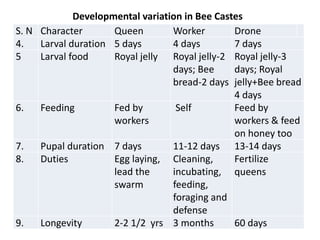
The document covers the identification, morphology, and structural adaptations of honey bees, detailing their systematic position within the order Hymenoptera and suborder Apocrita. It describes various honey bee species, their characteristics, differences among castes (queen, worker, and drone), and key morphological features including eyes, mouthparts, legs, wings, and abdomen. Additionally, it summarizes the life history and developmental variations among the different bee castes.