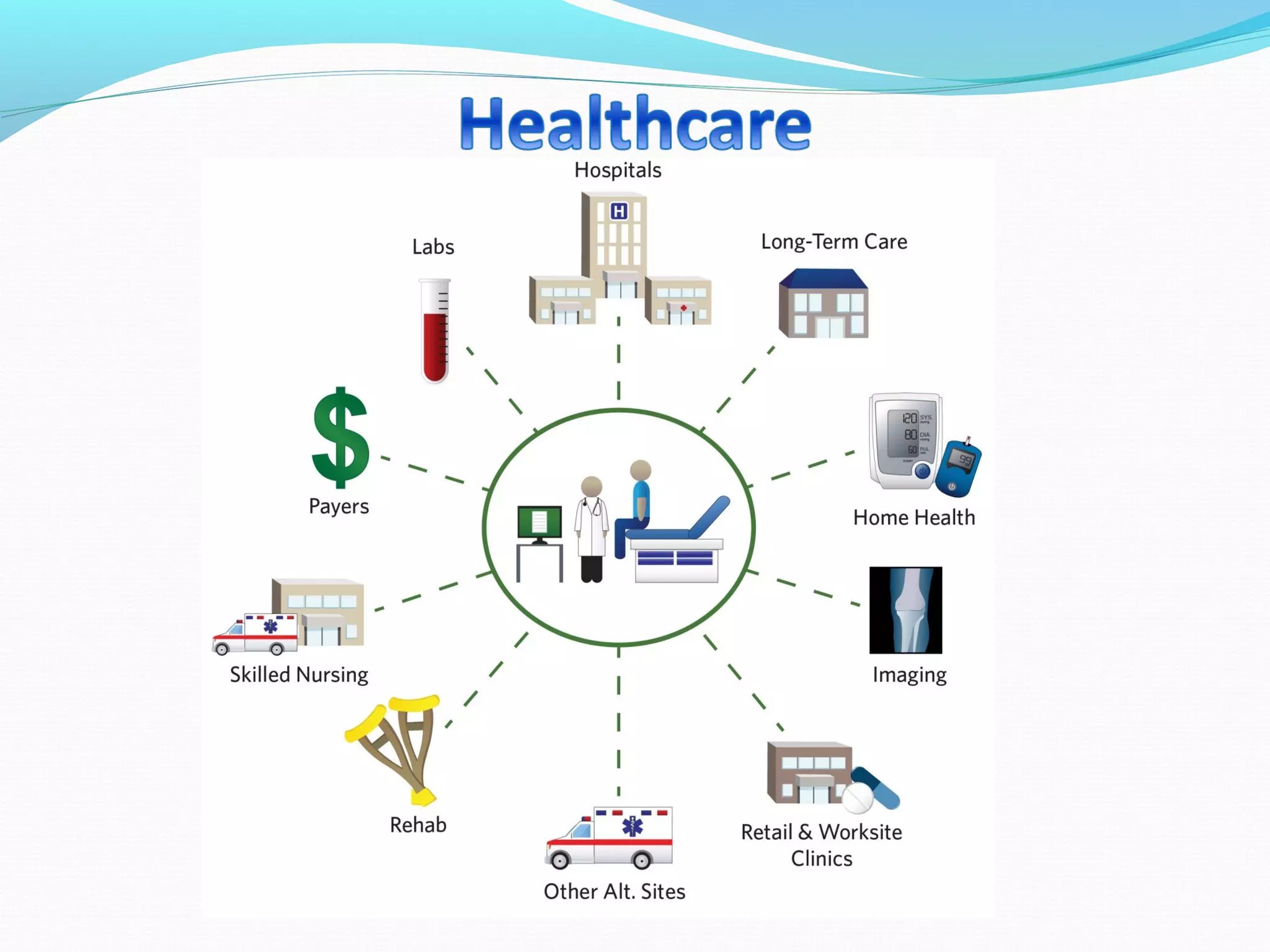
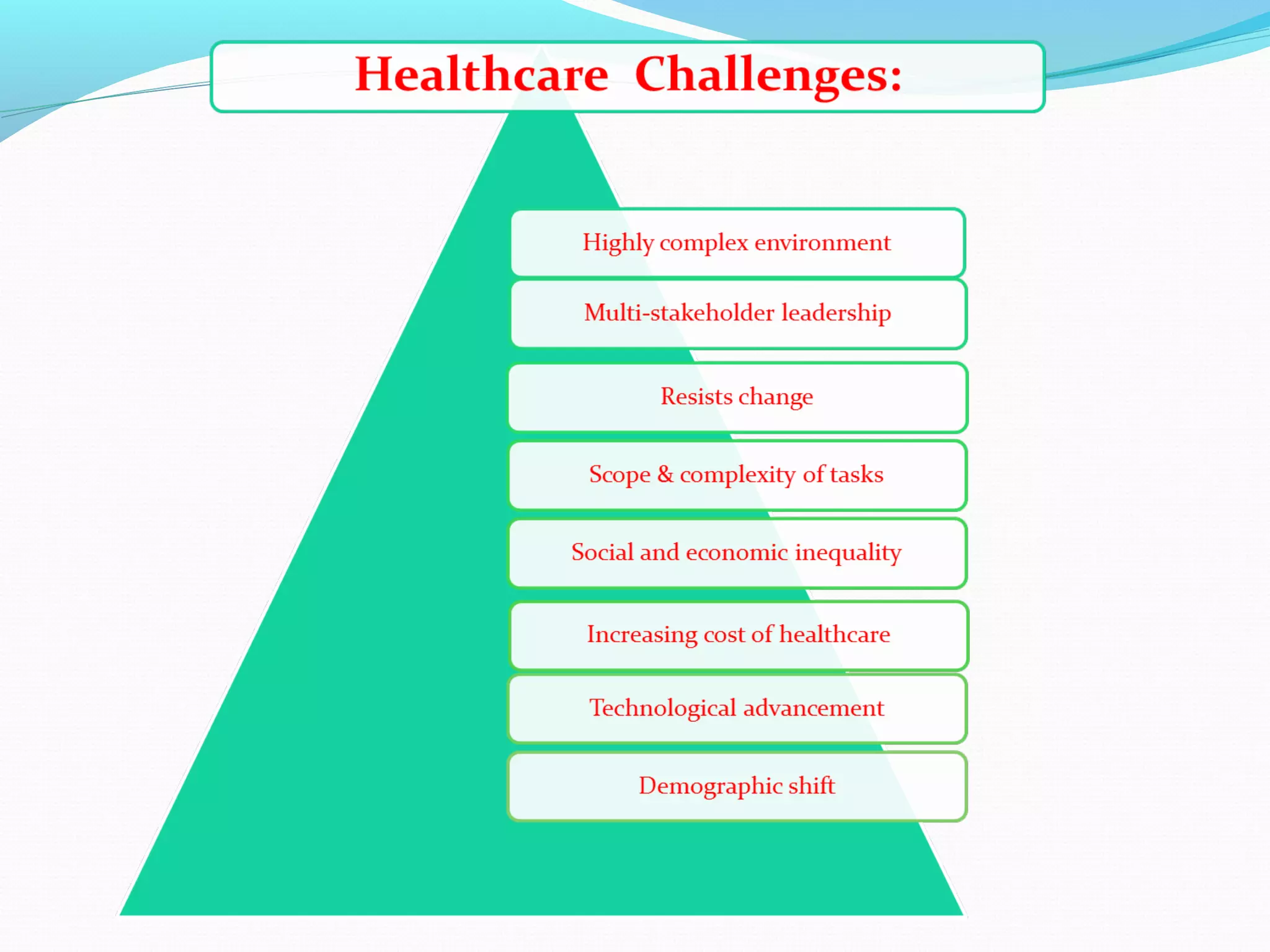
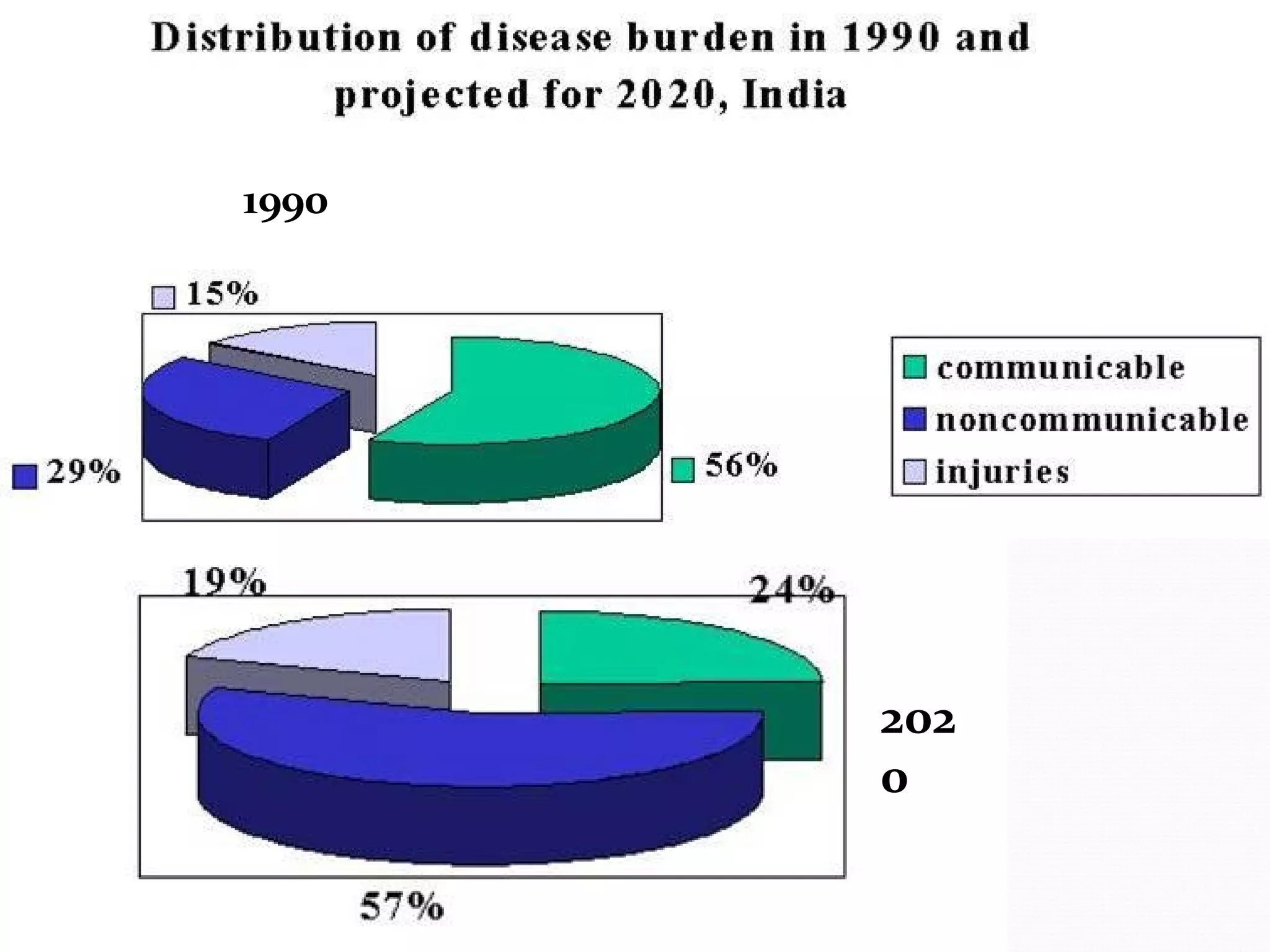
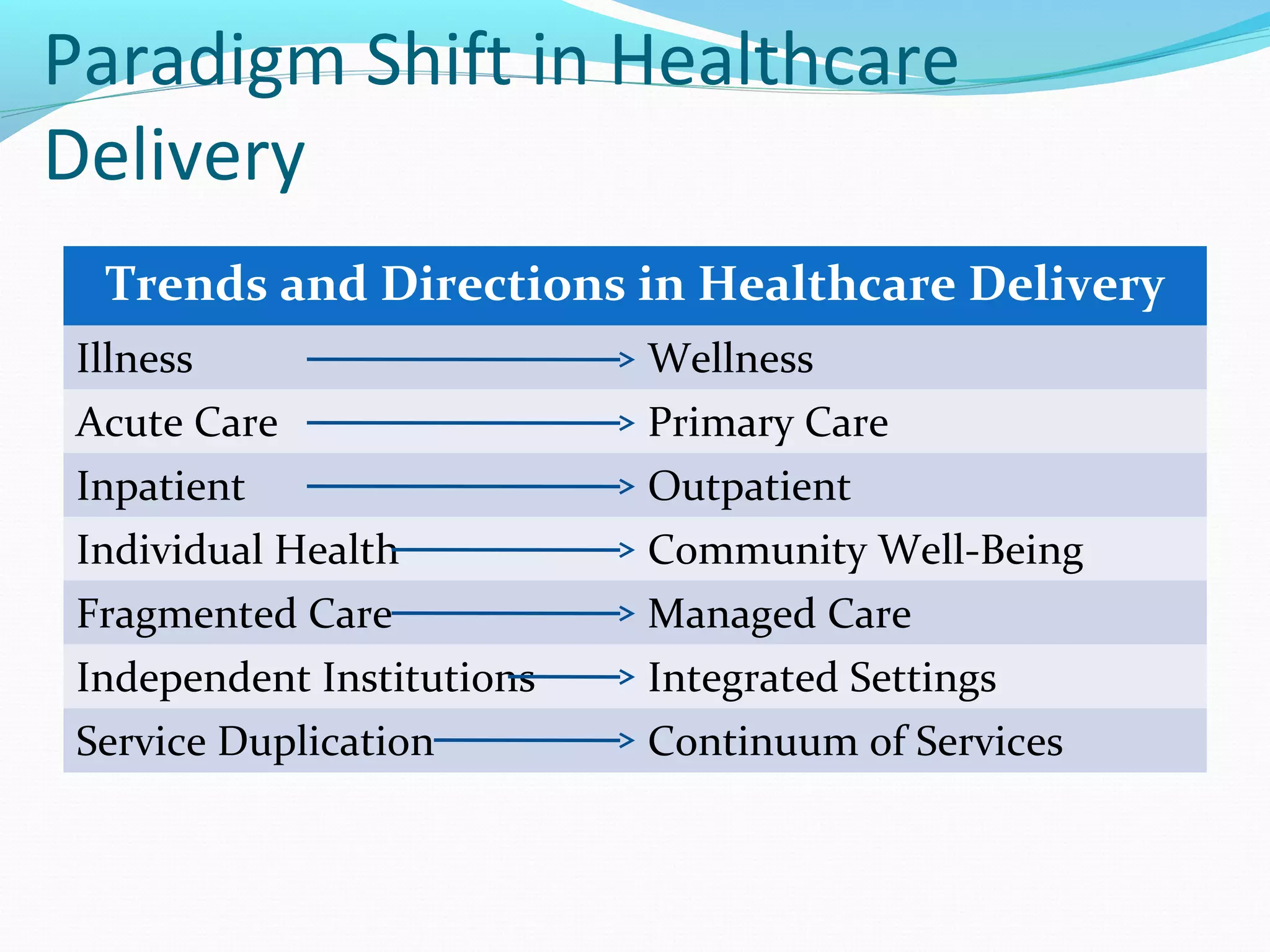
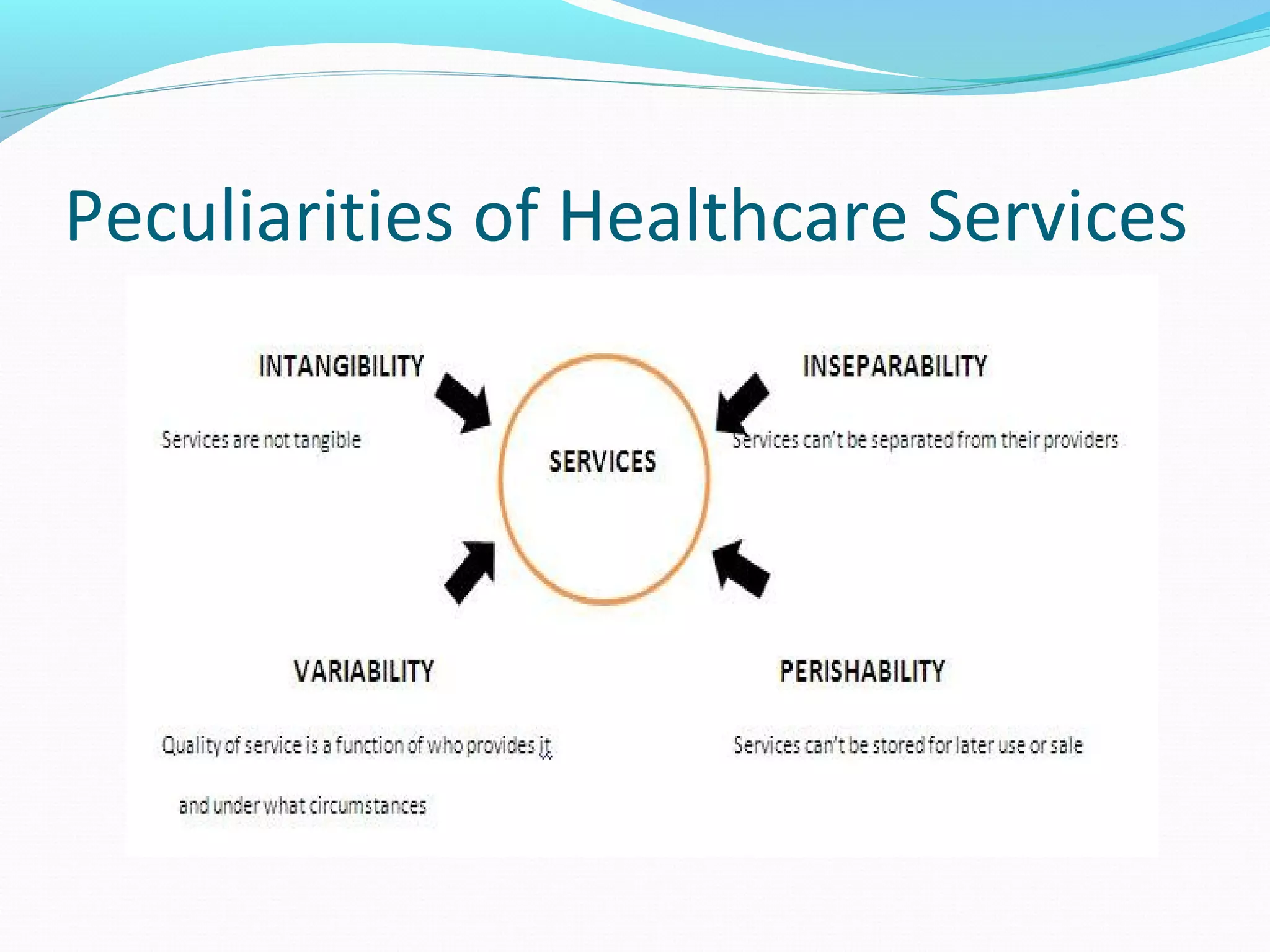
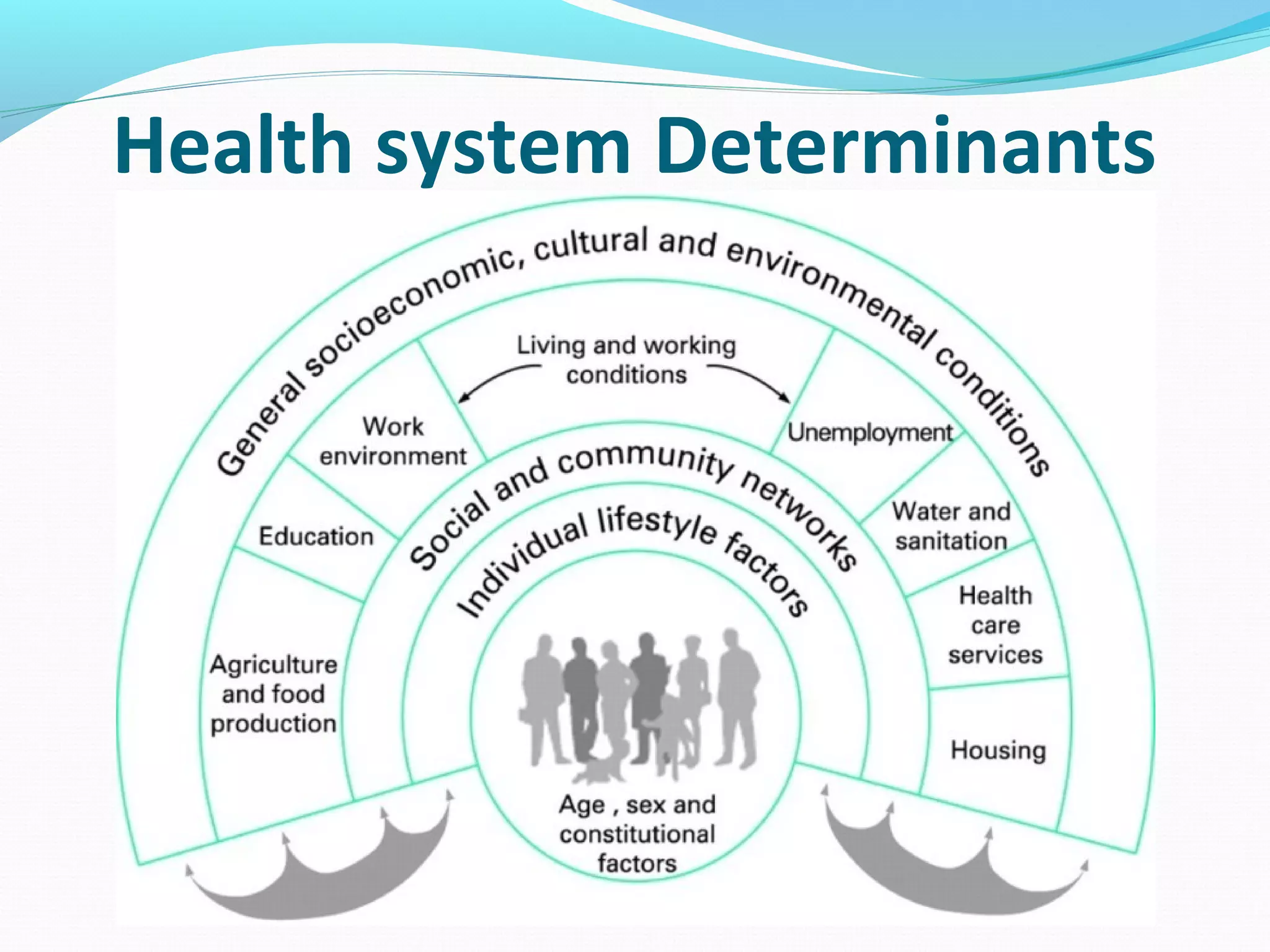
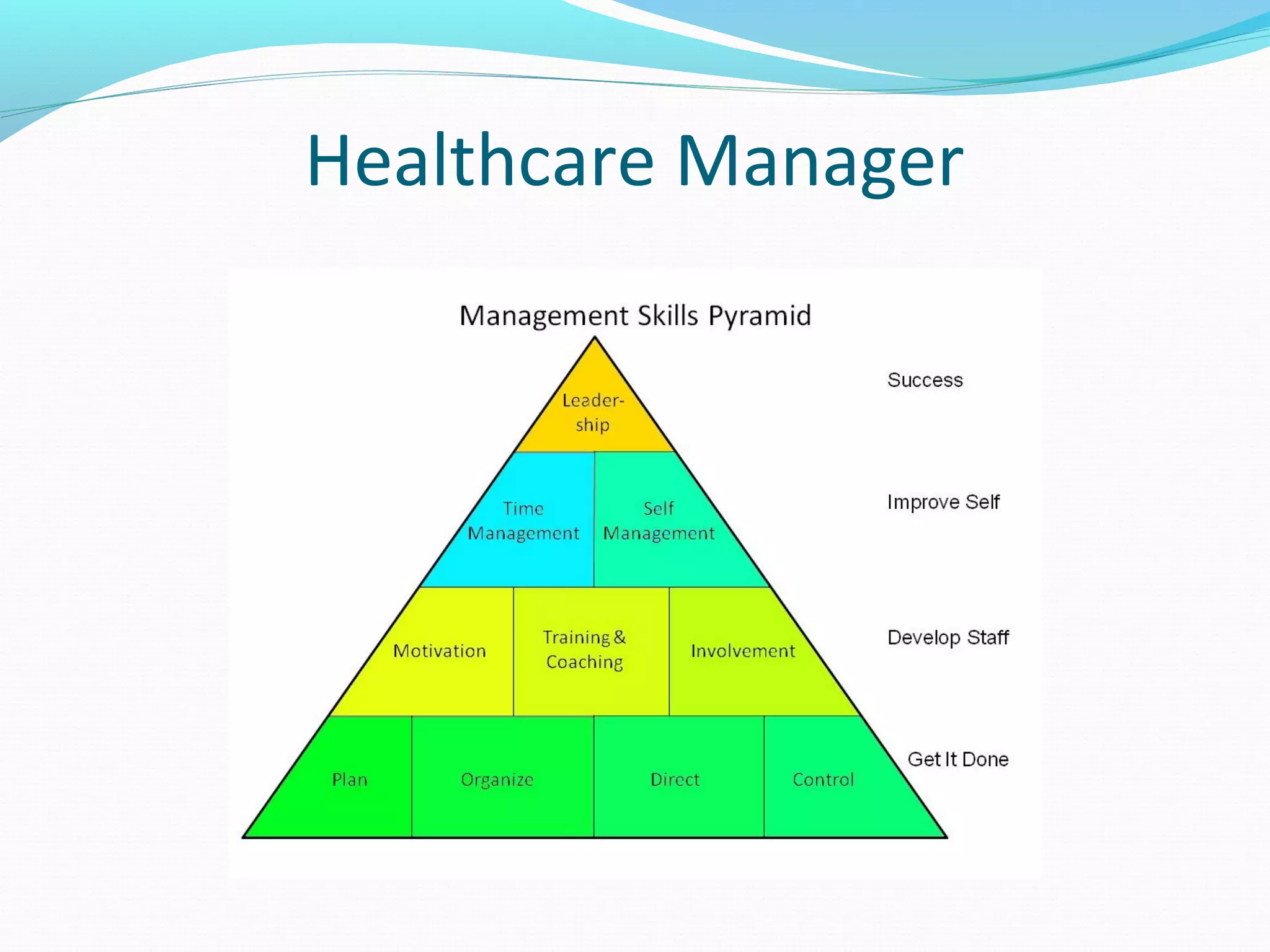
The document discusses healthcare in India. It notes that primary challenges include access, as 70% of India's population lives in rural areas but most doctors and hospitals are urban. Public health expenditure was 0.84% of GDP in 2004-05, rising to 1.1% in 2008-09. India faces twin epidemics of communicable and non-communicable diseases. The healthcare system is shifting from illness to wellness and from acute to primary care. Management is strongly tied to outcomes and satisfaction. The role of healthcare managers includes professional strategist, resourceful leadership, and facilitator.