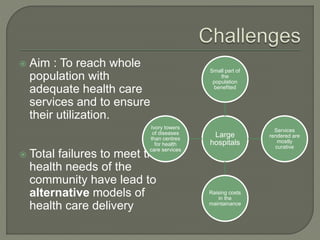
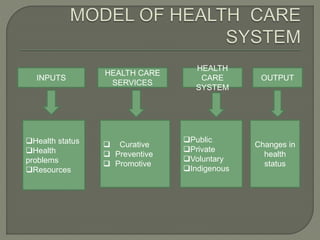
The document discusses India's health care delivery system. It notes that the system is made up of resources that are distributed to provide health services to the population. The goals of the system are to improve population health status, patient experience of care, reduce the economic burden of illness, and promote social justice and equity in health. The system aims to provide adequate health care services to the entire population. It discusses the various inputs, including health status, health problems, and resources, as well as the public, private, voluntary, and indigenous sectors that provide health care services and influence health outcomes.