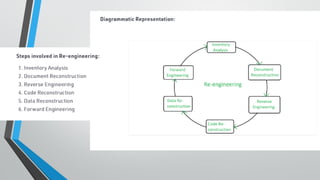
This document provides an introduction to software engineering. It defines software engineering as the systematic approach to designing, developing, operating, and maintaining software. It discusses the need for software engineering due to past software crises where projects regularly failed or went over budget. The document outlines objectives of software engineering such as maintainability, correctness, reusability, and reliability. It also distinguishes between a program and software product and discusses challenges in software engineering.